Cathelicidin-HG Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Platelet Dysfunction by Inhibiting GPVI-Mediated Platelet Activation
- PMID: 38840901
- PMCID: PMC11151873
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0381
Cathelicidin-HG Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Platelet Dysfunction by Inhibiting GPVI-Mediated Platelet Activation
Abstract
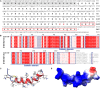
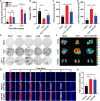
Platelet activation contributes to sepsis development, leading to microthrombosis and increased inflammation, which results in disseminated intravascular coagulation and multiple organ dysfunction. Although Cathelicidin can alleviate sepsis, its role in sepsis regulation remains largely unexplored. In this study, we identified Cath-HG, a novel Cathelicidin from Hylarana guentheri skin, and analyzed its structure using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The modulatory effect of Cath-HG on the symptoms of mice with sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture was evaluated in vivo, and the platelet count, degree of organ damage, and microthrombosis were measured. The antiplatelet aggregation activity of Cath-HG was studied in vitro, and its target was verified. Finally, we further investigated whether Cath-HG could regulate thrombosis in vivo in a FeCl3 injury-induced carotid artery model. The results showed that Cath-HG exhibited an α-helical structure in sodium dodecyl sulfate solution and effectively reduced organ inflammation and damage, improving survival in septic mice. It alleviated sepsis-induced thrombocytopenia and microthrombosis. In vitro, Cath-HG specifically inhibited collagen-induced platelet aggregation and modulated glycoprotein VI (GPVI) signaling pathways. Dot blotting, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and pull-down experiments confirmed GPVI as the target of Cath-HG. Molecular docking and amino acid residue truncations/mutations identified crucial sites of Cath-HG. These findings suggest that GPVI represents a promising therapeutic target for sepsis, and Cath-HG may serve as a potential treatment for sepsis-related thrombocytopenia and thrombotic events. Additionally, identifying Cath-HG as a GPVI inhibitor provides insights for developing novel antithrombotic therapies targeting platelet activation mediated by GPVI.
Copyright © 2024 Weichen Xiong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: A patent was filed based on this work.
Figures




References
-
- Poll T, Shankar-Hari M, Wiersinga WJ. The immunology of sepsis. Immunity. 2021;54(11):2450–2464. - PubMed
-
- Iba T, Levy JH, Warkentin TE, Thachil J, Poll T, Levi M, Scientific and Standardization Committee on DIC, and the Scientific and Standardization Committee on Perioperative and Critical Care of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis . Diagnosis and management of sepsis-induced coagulopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Thromb Haemost. 2019;17(11):1989–1994. - PubMed
-
- Iba T, Watanabe E, Umemura Y, Wada T, Hayashida K, Kushimoto S, Japanese Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guideline Working Group for disseminated intravascular coagulation, Wada H. Sepsis-associated disseminated intravascular coagulation and its differential diagnoses. J Intensive Care. 2019;7(1):32. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

