Inflammatory activity evaluation in patients with axial spondyloarthritis using MRI relaxometry and mucosal-associated invariant T cells
- PMID: 38840918
- PMCID: PMC11150633
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1391280
Inflammatory activity evaluation in patients with axial spondyloarthritis using MRI relaxometry and mucosal-associated invariant T cells
Abstract
Background: Currently, there is a lack of an objective quantitative measure to comprehensively evaluate the inflammatory activity of axSpA, which poses certain challenges in accurately assessing the disease activity.
Objective: To explore the value of combined-parameter models of sacroiliac joints (SIJs) MRI relaxometry and peripheral blood Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells in evaluating the inflammatory activity of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA).
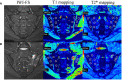
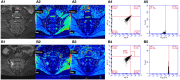
Methods: This retrospective clinical study included 88 axSpA patients (median age 31.0 (22.0, 41.8) years, 21.6% females) and 20 controls (median age 28.0 (20.5, 49.5) years, 40.0% females). The axSpA group was classified into active subgroup (n=50) and inactive subgroup (n=38) based on ASDAS-CRP. All participants underwent SIJs MRI examination including T1 and T2* mapping, and peripheral blood flow cytometry analysis of MAIT cells (defined as CD3+Vα7.2+CD161+) and their activation markers (CD69). The T1 and T2* values, as were the percentages of MAIT cells and CD69+MAIT cells were compared between different groups. Combined-parameter models were established using logistic regression, and ROC curves were employed to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy.
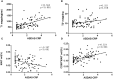
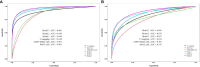
Results: The T1 values of SIJs and %CD69+MAIT cells in the axSpA group and its subgroup were higher than the control group (p<0.05), while %MAIT cells were lower than the control group (p<0.05). The T1 values and %CD69+MAIT cells correlated positively, while %MAIT cells correlated negatively, with the ASDAS-CRP (r=0.555, 0.524, -0.357, p<0.001). Between the control and axSpA groups, and between the inactive and active subgroups, the combined-parameter model T1 mapping+%CD69+MAIT cells has the best efficacy (AUC=0.959, 0.879, sensibility=88.6, 70%, specificity=95.0, 94.7%, respectively).
Conclusion: The combined-parameter model T1 mapping+%CD69+MAIT cells allows a more accurate evaluation of the level of inflammatory activity.
Keywords: T1 mapping; axial spondyloarthritis; combined-parameter model; magnetic resonance; mucosal-associated invariant T cells.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Zheng, Chen, Lin, Dai, Gao, Chen, Ma and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Marzo-Ortega H, McGonagle D, O’Connor P, Hensor EM, Bennett AN, Green MJ, et al. . Baseline and 1-year magnetic resonance imaging of the sacroiliac joint and lumbar spine in very early inflammatory back pain. Relationship between symptoms, HLA-B27 and disease extent and persistence. Ann Rheum Dis. (2009) 68(11):1721–7. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.097931 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ramiro S, van der Heijde D, van Tuberen A, Stolwijk C, Dougados M, van den Bosch F, et al. . Higher disease activity leads to more structural damage in the spine in ankylosing spondylitis: 12-year longitudinal data from the OASIS cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. (2014) 73 (8):1455–61. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205178 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

