The role of galectins in mediating the adhesion of circulating cells to vascular endothelium
- PMID: 38840921
- PMCID: PMC11150550
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395714
The role of galectins in mediating the adhesion of circulating cells to vascular endothelium
Abstract
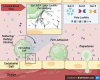
Vascular cell adhesion is a complex orchestration of events that commonly feature lectin-ligand interactions between circulating cells, such as immune, stem, and tumor cells, and endothelial cells (ECs) lining post-capillary venules. Characteristically, circulating cell adherence to the vasculature endothelium is initiated through interactions between surface sialo-fucosylated glycoprotein ligands and lectins, specifically platelet (P)- or endothelial (E)-selectin on ECs or between leukocyte (L)-selectin on circulating leukocytes and L-selectin ligands on ECs, culminating in circulating cell extravasation. This lectin-ligand interplay enables the migration of immune cells into specific tissue sites to help maintain effective immunosurveillance and inflammation control, the homing of stem cells to bone marrow or tissues in need of repair, and, unfortunately, in some cases, the dissemination of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) to distant metastatic sites. Interestingly, there is a growing body of evidence showing that the family of β-galactoside-binding lectins, known as galectins, can also play pivotal roles in the adhesion of circulating cells to the vascular endothelium. In this review, we present contemporary knowledge on the significant roles of host- and/or tumor-derived galectin (Gal)-3, -8, and -9 in facilitating the adhesion of circulating cells to the vascular endothelium either directly by acting as bridging molecules or indirectly by triggering signaling pathways to express adhesion molecules on ECs. We also explore strategies for interfering with galectin-mediated adhesion to attenuate inflammation or hinder the metastatic seeding of CTCs, which are often rich in galectins and/or their glycan ligands.
Keywords: cell adhesion; endothelial cells; galectin-3; galectin-8; galectin-9.
Copyright © 2024 Souchak, Mohammed, Lau and Dimitroff.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extravasation of immune and tumor cells from an endothelial perspective.J Cell Sci. 2024 Nov 1;137(21):jcs262066. doi: 10.1242/jcs.262066. Epub 2024 Nov 12. J Cell Sci. 2024. PMID: 39530179 Review.
-
Vascular Endothelial Galectins in Leukocyte Trafficking.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 1;12:687711. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.687711. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34140956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis: a novel function for the "tandem-repeat" lectin galectin-8.FASEB J. 2011 Jan;25(1):242-54. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-144907. Epub 2010 Sep 27. FASEB J. 2011. PMID: 20876211
-
Galectin-8: a matricellular lectin with key roles in angiogenesis.Glycobiology. 2014 Oct;24(10):907-14. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwu054. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Glycobiology. 2014. PMID: 24939370 Review.
-
Serum galectin-2, -4, and -8 are greatly increased in colon and breast cancer patients and promote cancer cell adhesion to blood vascular endothelium.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Nov 15;17(22):7035-46. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1462. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21933892
Cited by
-
Research progress of galectins in glioma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 4;16(1):1003. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02318-4. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40467873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of Intracellular Galectin-8 and -9 in Endometrial Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 24;25(13):6907. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136907. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000016 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Adhesiveness of Blood Cells Induced by Mercury Chloride: Protective Effect of Hydroxytyrosol.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Dec 20;13(12):1576. doi: 10.3390/antiox13121576. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765902 Free PMC article.
-
Glymphatic activity in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia: Link with vascular function and astrocytic activation.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Aug;21(8):e70561. doi: 10.1002/alz.70561. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 40791104 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying septic shock subgroups to tailor fluid strategies through multi-omics integration.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 19;15(1):9028. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53239-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39424794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rutledge NS, Muller WA. Understanding molecules that mediate leukocyte extravasation. Curr Pathobiol. Rep. (2020) 8:25–35. doi: 10.1007/s40139-020-00207-9 - DOI
-
- Alberts B. Molecular biology of the cell. Sixth edition Vol. 1. New York, NY: Garland Science, Taylor and Francis Group; (2015). volume (various pagings) p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

