Assessing the Premedication Properties of Sublingual Melatonin in Young Women Undergoing Cesarean Section With Spinal Anesthesia: A Double-Blind Randomized Study
- PMID: 38841008
- PMCID: PMC11150981
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.59710
Assessing the Premedication Properties of Sublingual Melatonin in Young Women Undergoing Cesarean Section With Spinal Anesthesia: A Double-Blind Randomized Study
Abstract
Introduction: Preoperative anxiety can negatively impact patient outcomes by influencing the intraoperative requirements for anesthetics and analgesics, increasing postoperative pain intensity, and augmenting the need for analgesia. Moreover, it may contribute to higher rates of postoperative morbidity and mortality following certain types of surgery. This study investigates the anxiolytic and sedative properties of sublingual melatonin as a premedication agent in young females undergoing cesarean section under spinal anesthesia.
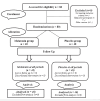
Methods: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted in Nasiriyah, Iraq. Eighty females were included, 40 in each group, based on specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. Premedication was administered in the morning, 60 minutes before the procedure. In the melatonin group (M), patients received 10 mg of sublingual melatonin, while the placebo group (P) received placebo premedication. Anxiety and sedation levels were evaluated three times: before taking premedication, five minutes before the insertion of the spinal needle, and one hour postoperatively, using the visual analog scale and Richmond Sedation Scale.
Results: The results show a highly significant P-value regarding anxiety levels between the M Group and P Group (p-value < 0.001). There was a significant difference in the median sedation scores between the studied groups at pre-spinal insertion and postoperatively (p-value < 0.001). The mean heart rate in the M Group was significantly lower than in the P Group (p-value = 0.0019). Significant differences were noted in systolic and diastolic blood pressures between the two groups, measured five minutes before and after spinal needle insertion (p-value < 0.001).
Conclusion: These findings contribute to understanding the impact of sublingual melatonin as an anxiolytic and sedative premedication agent on patients undergoing elective cesarean sections under spinal anesthesia. Further research is warranted to fully elucidate the benefits and implications of melatonin administration in such procedures.
Keywords: melatonin; premedication; preoperative anxiety; sedation; spinal anesthesia.
Copyright © 2024, Alkhfaji et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Melatonin as a Premedication Agent in Caesarean Section on Blood Loss and Postoperative Pain Level.Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2023 Dec 12;2023:8102111. doi: 10.1155/2023/8102111. eCollection 2023. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 38116042 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Analgesic Efficacy of Melatonin in Patients Undergoing Cesarean Section Under S pinal Anesthesia: A Prospective Randomized Double-blind Study.Iran J Pharm Res. 2016 Fall;15(4):963-971. Iran J Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 28243296 Free PMC article.
-
Premedication effect of melatonin on propofol induction dose for anesthesia, anxiety, orientation and sedation after abdominal surgery: a double-blinded randomized trial.Med Gas Res. 2019 Apr-Jun;9(2):62-67. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.260646. Med Gas Res. 2019. PMID: 31249253 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of melatonin on anxiety and pain scores of patients, intraocular pressure, and operating conditions during cataract surgery under topical anesthesia.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2013 Jul;61(7):319-24. doi: 10.4103/0301-4738.99637. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 23552356 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Comprehensive Review on the Role of Melatonin's Anesthetic Applications in Pediatric Care.Cureus. 2024 May 18;16(5):e60575. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60575. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38894785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin's Impact on Wound Healing.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 2;13(10):1197. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101197. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456451 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Premedication with midazolam prior to caesarean section has no neonatal adverse effects. Senel AC, Mergan F. http://10.1016/j.bjan.2012.08.003. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2014;64:16–21. - PubMed
-
- Managing anxiety in the elective surgical patient. Pritchard MJ. http://10.12968/bjon.2009.18.7.41655. Br J Nurs. 2009;18:416–419. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources