Knowledge domains and emerging trends in radiotherapy in oesophageal cancer from 2004 to 2023: a bibliometric analysis and visualization study
- PMID: 38842165
- PMCID: PMC11262863
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrae040
Knowledge domains and emerging trends in radiotherapy in oesophageal cancer from 2004 to 2023: a bibliometric analysis and visualization study
Abstract
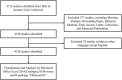
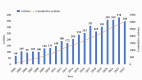
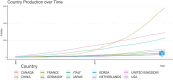
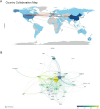
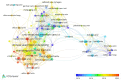
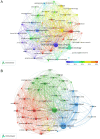
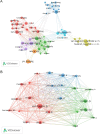
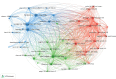
Esophageal cancer (EC) is a malignant tumour with high morbidity and mortality rates. Recent studies have shown that much progress has been made in the research of radiotherapy in EC. This study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the knowledge structure and research hotspots of radiotherapy in EC through bibliometrics. Publications related to radiotherapy in EC from 2014 to 2023 were searched on the web of science core collection database. VOSviewers, CiteSpace and R package 'bibliometrix' were used to conduct this bibliometric analysis. In total, 4258 articles from 76 countries led by China and the USA were included. The Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences-Peking Union Medical College has the highest number of publications. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics is the most popular journal and also the most co-cited journal in this field. These publications come from 21 972 authors among which Liao Zhongxing had published the most papers and Cooper JS was co-cited most often. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and strategies based on it are the main topics in this research field. 'IMRT' and 'immunotherapy' are the primary keywords of emerging research hotspots. This is a bibliometric study that comprehensively summarizes the research trends and developments of radiotherapy in EC. This information identifies recent research frontiers and hot directions, which will provide a reference for scholars studying radiotherapy in EC.
Keywords: CiteSpace; VOSviewers; bibliometrics; esophageal cancer; radiotherapy.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Knowledge Mapping of Exosomes in Autoimmune Diseases: A Bibliometric Analysis (2002-2021).Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 22;13:939433. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.939433. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35935932 Free PMC article.
-
Liver cancer from the perspective of single-cell sequencing: a review combined with bibliometric analysis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun 24;150(6):316. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05855-7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38910204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hotspots and frontiers of autophagy and chemotherapy in lung cancer: a bibliometric and visualization analysis from 2003 to 2023.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;398(2):1583-1595. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03354-7. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39120721
-
Global trends and hotspots of treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A bibliometric and visualization analysis (2010-2023).World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Oct 7;29(37):5339-5360. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i37.5339. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37899789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knowledge mapping of immunotherapy in cervical carcinoma: a bibliometric analysis (2000-2023).Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 9;14:1328103. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1328103. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38264659 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 202 340 160/Scientific Research Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission
- 23KFL105/Science and Technology Development Project of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- SGZXY-202201/Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine Project of Shuguang Hospital affiliated with Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

