COVID-19 Vaccination Coverage and Factors Associated With Vaccine Uptake Among People With HIV
- PMID: 38842808
- PMCID: PMC11157350
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.15220
COVID-19 Vaccination Coverage and Factors Associated With Vaccine Uptake Among People With HIV
Abstract
Importance: People with HIV (PWH) may be at increased risk for severe outcomes with COVID-19 illness compared with people without HIV. Little is known about COVID-19 vaccination coverage and factors associated with primary series completion among PWH.
Objectives: To evaluate COVID-19 vaccination coverage among PWH and examine sociodemographic, clinical, and community-level factors associated with completion of the primary series and an additional primary dose.
Design, setting, and participants: This retrospective cohort study used electronic health record data to assess COVID-19 vaccination information from December 14, 2020, through April 30, 2022, from 8 health care organizations of the Vaccine Safety Datalink project in the US. Participants were adults diagnosed with HIV on or before December 14, 2020, enrolled in a participating site.
Main outcomes and measures: The percentage of PWH with at least 1 dose of COVID-19 vaccine and PWH who completed the COVID-19 vaccine primary series by December 31, 2021, and an additional primary dose by April 30, 2022. Rate ratios (RR) and 95% CIs were estimated using Poisson regression models for factors associated with completing the COVID-19 vaccine primary series and receiving an additional primary dose.
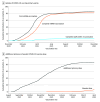
Results: Among 22 058 adult PWH (mean [SD] age, 52.1 [13.3] years; 88.8% male), 90.5% completed the primary series by December 31, 2021. Among 18 374 eligible PWH who completed the primary series by August 12, 2021, 15 982 (87.0%) received an additional primary dose, and 4318 (23.5%) received a booster dose by April 30, 2022. Receipt of influenza vaccines in the last 2 years was associated with completion of the primary series (RR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.15-1.20) and an additional primary dose (RR, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.54-1.69). PWH with uncontrolled viremia (HIV viral load ≥200 copies/mL) (eg, RR, 0.90 [95% CI, 0.85-0.95] for viral load 200-10 000 copies/mL vs undetected or <200 copies/mL for completing the primary series) and Medicaid insurance (eg, RR, 0.89 [95% CI, 0.87-0.90] for completing the primary series) were less likely to be fully vaccinated. By contrast, greater outpatient utilization (eg, RR, 1.07 [95% CI, 1.05-1.09] for ≥7 vs 0 visits for primary series completion) and residence in counties with higher COVID-19 vaccine coverage (eg, RR, 1.06 [95% CI, 1.03-1.08] for fourth vs first quartiles for primary series completion) were associated with primary series and additional dose completion (RRs ranging from 1.01 to 1.21).
Conclusions and relevance: Findings from this cohort study suggest that, while COVID-19 vaccination coverage was high among PWH, outreach efforts should focus on those who did not complete vaccine series and those who have uncontrolled viremia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Boulle A, Davies MA, Hussey H, et al. ; Western Cape Department of Health in collaboration with the National Institute for Communicable Diseases, South Africa . Risk factors for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) death in a population cohort study from the Western Cape Province, South Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;73(7):e2005-e2015. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1198 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Geretti AM, Stockdale AJ, Kelly SH, et al. . Outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) related hospitalization among people with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in the ISARIC World Health Organization (WHO) clinical characterization protocol (UK): a prospective observational study. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;73(7):e2095-e2106. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1605 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

