Replication protein A dynamically re-organizes on primer/template junctions to permit DNA polymerase δ holoenzyme assembly and initiation of DNA synthesis
- PMID: 38842913
- PMCID: PMC11260492
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae475
Replication protein A dynamically re-organizes on primer/template junctions to permit DNA polymerase δ holoenzyme assembly and initiation of DNA synthesis
Abstract
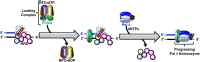
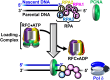
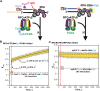
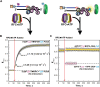
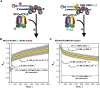
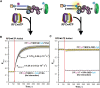
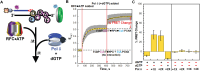
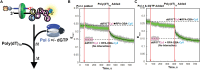
DNA polymerase δ (pol δ) holoenzymes, comprised of pol δ and the processivity sliding clamp, PCNA, carry out DNA synthesis during lagging strand replication, initiation of leading strand replication, and the major DNA damage repair and tolerance pathways. Pol δ holoenzymes are assembled at primer/template (P/T) junctions and initiate DNA synthesis in a stepwise process involving the major single strand DNA (ssDNA)-binding protein complex, RPA, the processivity sliding clamp loader, RFC, PCNA and pol δ. During this process, the interactions of RPA, RFC and pol δ with a P/T junction all significantly overlap. A burning issue that has yet to be resolved is how these overlapping interactions are accommodated during this process. To address this, we design and utilize novel, ensemble FRET assays that continuously monitor the interactions of RPA, RFC, PCNA and pol δ with DNA as pol δ holoenzymes are assembled and initiate DNA synthesis. Results from the present study reveal that RPA remains engaged with P/T junctions throughout this process and the RPA•DNA complexes dynamically re-organize to allow successive binding of RFC and pol δ. These results have broad implications as they highlight and distinguish the functional consequences of dynamic RPA•DNA interactions in RPA-dependent DNA metabolic processes.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct, ensemble FRET approaches to monitor transient state kinetics of human DNA polymerase δ holoenzyme assembly and initiation of DNA synthesis.Methods Enzymol. 2024;705:271-309. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2024.08.002. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Methods Enzymol. 2024. PMID: 39389667
-
Interplay of macromolecular interactions during assembly of human DNA polymerase δ holoenzymes and initiation of DNA synthesis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 9:2023.05.09.539896. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.09.539896. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37215012 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A human high-fidelity DNA polymerase holoenzyme has a wide range of lesion bypass activities.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 8;53(13):gkaf646. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf646. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40671520 Free PMC article.
-
Bulk synthesis and beyond: The roles of eukaryotic replicative DNA polymerases.DNA Repair (Amst). 2024 Sep;141:103740. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2024.103740. Epub 2024 Jul 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2024. PMID: 39096696 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of the human CTF18-RFC clamp loader bound to PCNA.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 24:2024.05.08.593111. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.08.593111. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40777363 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Direct, ensemble FRET approaches to monitor transient state kinetics of human DNA polymerase δ holoenzyme assembly and initiation of DNA synthesis.Methods Enzymol. 2024;705:271-309. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2024.08.002. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Methods Enzymol. 2024. PMID: 39389667
-
Chemotherapeutic 6-thio-2'-deoxyguanosine selectively targets and inhibits telomerase by inducing a non-productive telomere-bound telomerase complex.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 27:2025.02.05.636339. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.05.636339. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39975053 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

