Bexotegrast in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The INTEGRIS-IPF Clinical Trial
- PMID: 38843105
- PMCID: PMC11351797
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202403-0636OC
Bexotegrast in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The INTEGRIS-IPF Clinical Trial
Abstract
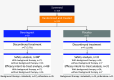
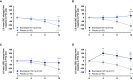
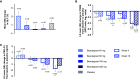
Rationale: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a rare and progressive disease that causes progressive cough, exertional dyspnea, impaired quality of life, and death. Objectives: Bexotegrast (PLN-74809) is an oral, once-daily, investigational drug in development for the treatment of IPF. Methods: This Phase-2a multicenter, clinical trial randomized participants with IPF to receive, orally and once daily, bexotegrast at 40 mg, 80 mg, 160 mg, or 320 mg, or placebo, with or without background IPF therapy (pirfenidone or nintedanib), in an approximately 3:1 ratio in each bexotegrast dose cohort, for at least 12 weeks. The primary endpoint was incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs). Exploratory efficacy endpoints included change from baseline in FVC, quantitative lung fibrosis (QLF) extent (%), and changes from baseline in fibrosis-related biomarkers. Measurements and Main Results: Bexotegrast was well tolerated, with similar rates of TEAEs in the pooled bexotegrast and placebo groups (62/89 [69.7%] and 21/31 [67.7%], respectively). Diarrhea was the most common TEAE; most participants with diarrhea also received nintedanib. Participants who were treated with bexotegrast experienced a reduction in FVC decline over 12 weeks compared with those who received placebo, with or without background therapy. A dose-dependent antifibrotic effect of bexotegrast was observed with QLF imaging, and a decrease in fibrosis-associated biomarkers was observed with bexotegrast versus placebo. Conclusions: Bexotegrast demonstrated a favorable safety and tolerability profile, up to 12 weeks for the doses studied. Exploratory analyses suggest an antifibrotic effect according to FVC, QLF imaging, and circulating levels of fibrosis biomarkers. Clinical trial registered with www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT04396756).
Keywords: IPF; efficacy; fibrotic disease; safety.
Figures

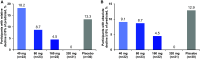
Comment in
-
INTEGRIS-IPF: A New Hope for Tomorrow.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Aug 15;210(4):374-375. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202407-1295ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38990732 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lederer DJ, Martinez FJ. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med . 2018;378:1811–1823. - PubMed

