Phased chromosome-scale genome assembly of an asexual, allopolyploid root-knot nematode reveals complex subgenomic structure
- PMID: 38843263
- PMCID: PMC11156385
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302506
Phased chromosome-scale genome assembly of an asexual, allopolyploid root-knot nematode reveals complex subgenomic structure
Abstract
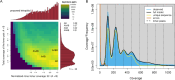
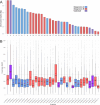
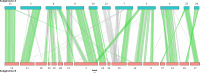
We present the chromosome-scale genome assembly of the allopolyploid root-knot nematode Meloidogyne javanica. We show that the M. javanica genome is predominantly allotetraploid, comprising two subgenomes, A and B, that most likely originated from hybridisation of two ancestral parental species. The assembly was annotated using full-length non-chimeric transcripts, comparison to reference databases, and ab initio prediction techniques, and the subgenomes were phased using ancestral k-mer spectral analysis. Subgenome B appears to show fission of chromosomal contigs, and while there is substantial synteny between subgenomes, we also identified regions lacking synteny that may have diverged in the ancestral genomes prior to or following hybridisation. This annotated and phased genome assembly forms a significant resource for understanding the origins and genetics of these globally important plant pathogens.
Copyright: © 2024 Winter et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Single, Shared Triploidy in Three Species of Parasitic Nematodes.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Jan 7;10(1):225-233. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400650. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 31694855 Free PMC article.
-
Hybridization and polyploidy enable genomic plasticity without sex in the most devastating plant-parasitic nematodes.PLoS Genet. 2017 Jun 8;13(6):e1006777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006777. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28594822 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide expert annotation of the epigenetic machinery of the plant-parasitic nematodes Meloidogyne spp., with a focus on the asexually reproducing species.BMC Genomics. 2018 May 3;19(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4686-x. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29724186 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and evolution of root-knot nematodes, genus Meloidogyne: new insights from the genomic era.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2013;51:203-20. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102300. Epub 2013 May 13. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2013. PMID: 23682915 Review.
-
Apomictic, polyphagous root-knot nematodes: exceptionally successful and damaging biotrophic root pathogens.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2001;39:53-77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.39.1.53. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2001. PMID: 11701859 Review.
Cited by
-
A trehalase-derived MAMP triggers LecRK-V-mediated immune responses in Arabidopsis.Sci Adv. 2025 Aug;11(31):eadv8896. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adv8896. Epub 2025 Jul 30. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40737394 Free PMC article.
-
High-fidelity annotated triploid genome of the quarantine root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne enterolobii.Sci Data. 2025 Jan 30;12(1):184. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-04434-w. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 39885189 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

