Telisotuzumab Vedotin Monotherapy in Patients With Previously Treated c-Met Protein-Overexpressing Advanced Nonsquamous EGFR-Wildtype Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Phase II LUMINOSITY Trial
- PMID: 38843488
- PMCID: PMC11361350
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.24.00720
Telisotuzumab Vedotin Monotherapy in Patients With Previously Treated c-Met Protein-Overexpressing Advanced Nonsquamous EGFR-Wildtype Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Phase II LUMINOSITY Trial
Abstract
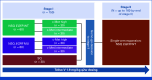
Purpose: Telisotuzumab vedotin (Teliso-V) is a c-Met-directed antibody-drug conjugate with a monomethyl auristatin E cytotoxic payload. The phase II LUMINOSITY trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03539536) aimed to identify the optimal c-Met protein-overexpressing non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) population for treatment with Teliso-V (stage I) and expand the selected group for efficacy evaluation (stage II). Stage II enrolled patients with nonsquamous epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-wildtype NSCLC.
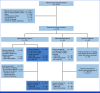
Methods: Eligible patients had locally advanced/metastatic c-Met protein-overexpressing NSCLC and ≤2 previous lines of therapy (including ≤1 line of systemic chemotherapy). c-Met protein overexpression in nonsquamous EGFR-wildtype NSCLC was defined as ≥25% tumor cells with 3+ staining (high [≥50% 3+]; intermediate [≥25%-<50%]). Teliso-V was administered at 1.9 mg/kg once every 2 weeks. The primary end point was overall response rate (ORR) by independent central review.
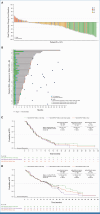
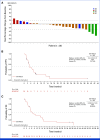
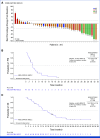
Results: In total, 172 patients with nonsquamous EGFR-wildtype NSCLC received Teliso-V in stages I and II. ORR was 28.6% (95% CI, 21.7 to 36.2; c-Met high, 34.6% [95% CI, 24.2 to 46.2]; c-Met intermediate, 22.9% [95% CI, 14.4 to 33.4]). The median duration of response was 8.3 months (95% CI, 5.6 to 11.3; c-Met high, 9.0 [95% CI, 4.2 to 13.0]; c-Met intermediate: 7.2 [95% CI, 5.3 to 11.5]). The median overall survival was 14.5 months (95% CI, 9.9 to 16.6; c-Met high, 14.6 [95% CI, 9.2 to 25.6]; c-Met intermediate, 14.2 [95% CI, 9.6 to 16.6]). The median progression-free survival was 5.7 months (95% CI, 4.6 to 6.9; c-Met high, 5.5 [95% CI, 4.1 to 8.3]; c-Met intermediate: 6.0 [95% CI, 4.5 to 8.1]). Most common any-grade treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were peripheral sensory neuropathy (30%), peripheral edema (16%), and fatigue (14%); the most common grade ≥3 AE was peripheral sensory neuropathy (7%).
Conclusion: Teliso-V was associated with durable responses in c-Met protein-overexpressing nonsquamous EGFR-wildtype NSCLC, especially in those with high c-Met. AEs were generally manageable.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Ma PC, Maulik G, Christensen J, et al. : c-Met: structure, functions and potential for therapeutic inhibition. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:309-325, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Gherardi E, Birchmeier W, Birchmeier C, et al. : Targeting MET in cancer: Rationale and progress. Nat Rev Cancer 12:89-103, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Wolf J, Seto T, Han JY, et al. : Capmatinib in MET exon 14-mutated or MET-amplified non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 383:944-957, 2020 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

