Mitochondrial lipidomes are tissue specific - low cholesterol contents relate to UCP1 activity
- PMID: 38843936
- PMCID: PMC11157264
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202402828
Mitochondrial lipidomes are tissue specific - low cholesterol contents relate to UCP1 activity
Abstract
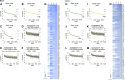
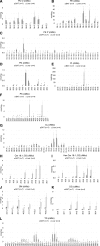
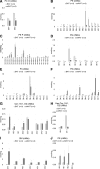
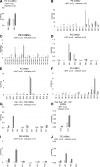
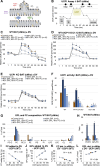
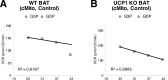
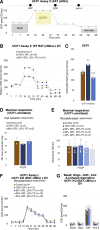
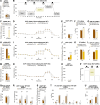
Lipid composition is conserved within sub-cellular compartments to maintain cell function. Lipidomic analyses of liver, muscle, white and brown adipose tissue (BAT) mitochondria revealed substantial differences in their glycerophospholipid (GPL) and free cholesterol (FC) contents. The GPL to FC ratio was 50-fold higher in brown than white adipose tissue mitochondria. Their purity was verified by comparison of proteomes with ER and mitochondria-associated membranes. A lipid signature containing PC and FC, calculated from the lipidomic profiles, allowed differentiation of mitochondria from BAT of mice housed at different temperatures. Elevating FC in BAT mitochondria prevented uncoupling protein (UCP) 1 function, whereas increasing GPL boosted it. Similarly, STARD3 overexpression facilitating mitochondrial FC import inhibited UCP1 function in primary brown adipocytes, whereas a knockdown promoted it. We conclude that the mitochondrial GPL/FC ratio is key for BAT function and propose that targeting it might be a promising strategy to promote UCP1 activity.
© 2024 Brunner et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Balboa E, Castro J, Pinochet MJ, Cancino GI, Matias N, Saez PJ, Martinez A, Alvarez AR, Garcia-Ruiz C, Fernandez-Checa JC, et al. (2017) Mln64 induces mitochondrial dysfunction associated with increased mitochondrial cholesterol content. Redox Biol 12: 274–284. 10.1016/j.redox.2017.02.024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
