Carborane Conjugates with Ibuprofen, Fenoprofen and Flurbiprofen: Synthesis, Characterization, COX Inhibition Potential and In Vitro Activity
- PMID: 38844420
- PMCID: PMC11694610
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202400018
Carborane Conjugates with Ibuprofen, Fenoprofen and Flurbiprofen: Synthesis, Characterization, COX Inhibition Potential and In Vitro Activity
Abstract
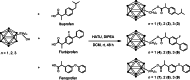
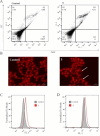
The most effective anticancer drugs currently entail substantial and formidable side effects, and resistance of tumors to chemotherapeutic agents is a further challenge. Thus, the search for new anticancer drugs as well as novel therapeutic methods is still extremely important. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can inhibit COX (cyclooxygenase), overexpressed in some tumors. Carboranes are emerging as promising pharmacophores. We have therefore combined both moieties in a single molecule to design drugs with a dual mode of action and enhanced effectiveness. The NSAIDs ibuprofen, flurbiprofen, and fenoprofen were connected with 1,2-dicarba-closo-dodecaborane(12) via methylene, ethylene or propylene spacers. Three sets of carborane-NSAID conjugates were synthesized and analyzed through multinuclear (1H, 11B, and 13C) NMR spectroscopy. Conjugates with methylene spacers exhibited the most potent COX inhibition potential, particularly conjugates with flurbiprofen and fenoprofen, displaying higher selectivity towards COX-1. Furthermore, conjugates with methylene and ethylene spacers were more efficient in suppressing the growth of human cancer cell lines than their propylene counterparts. The carborane-flurbiprofen conjugate with an ethylene spacer was the most efficient and selective toward the COX-2-negative cell line HCT116. Its mode of action was basically cytostatic with minor contribution of apoptotic cell death and dominance of cells trapped in the division process.
Keywords: carboranes; drug conjugates; fenoprofen; flurbiprofen; ibuprofen.
© 2024 The Authors. ChemMedChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Carborane-Based Analogs of Celecoxib and Flurbiprofen, their COX Inhibition Potential, and COX Selectivity Index.ChemMedChem. 2025 Jun 2;20(11):e202500166. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202500166. Epub 2025 May 4. ChemMedChem. 2025. PMID: 40128115 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of new ibuprofen hybrid conjugates as potential anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents.Future Med Chem. 2020 Aug;12(15):1369-1386. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2020-0109. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Future Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32689823
-
Synthesis, molecular dynamics simulation, and evaluation of biological activity of novel flurbiprofen and ibuprofen-like compounds.J Mol Recognit. 2024 Sep;37(5):e3089. doi: 10.1002/jmr.3089. Epub 2024 Jun 18. J Mol Recognit. 2024. PMID: 38894531
-
Arylpropionic acid-derived NSAIDs: New insights on derivatization, anticancer activity and potential mechanism of action.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Nov;92:103224. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103224. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31491568 Review.
-
[A novel class of anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs--NO-donating NSAIDs].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007 Apr;42(4):352-7. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17633199 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Carborane-Based Analogs of Celecoxib and Flurbiprofen, their COX Inhibition Potential, and COX Selectivity Index.ChemMedChem. 2025 Jun 2;20(11):e202500166. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202500166. Epub 2025 May 4. ChemMedChem. 2025. PMID: 40128115 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

