Durable control of psoriatic arthritis with guselkumab across domains and patient characteristics: post hoc analysis of a phase 3 study
- PMID: 38844682
- PMCID: PMC11269379
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-024-06991-8
Durable control of psoriatic arthritis with guselkumab across domains and patient characteristics: post hoc analysis of a phase 3 study
Abstract
Objectives: Evaluate patterns of stringent disease control with 2 years of guselkumab across key disease-identified domains and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in subgroups of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) defined by baseline characteristics.
Method: This post hoc analysis of DISCOVER-2 (Clinicaltrials.gov NCT03158285) evaluated biologic-naïve PsA patients (≥ 5 swollen/ ≥ 5 tender joints, C-reactive protein [CRP] ≥ 0.6 mg/dL) randomized to guselkumab every 4 weeks (Q4W); guselkumab at Weeks 0 and 4, then Q8W; or placebo with crossover to guselkumab Q4W at Week 24. Achievement of American College of Rheumatology 50/70% improvement (ACR50/70), Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA) 0, dactylitis/enthesitis resolution, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)-Fatigue response (≥ 4-point improvement), HAQ-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) response (≥ 0.35-point improvement), PsA Disease Activity Score (PASDAS) low disease activity (LDA), and minimal disease activity (MDA) was assessed at Weeks 24, 52, and 100 in subgroups defined by sex and baseline medication use, body mass index, PsA duration, swollen/tender joints, CRP, and psoriasis severity/extent. Patients with missing categorical response data were considered nonresponders.
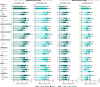
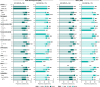
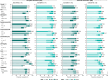
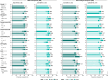
Results: 442/493 (90%) guselkumab-randomized patients completed treatment through Week 100. Significant multi-domain efficacy of guselkumab versus placebo was shown across adequately sized patient subgroups. A pattern of continuous improvement was observed across key PsA domains and PROs within patient subgroups: 65%-85% of guselkumab-randomized patients had enthesitis/dactylitis resolution, 50%-70% achieved complete skin clearance, 60%-80% reported meaningful improvements in function/fatigue, 40%-65% achieved PASDAS LDA, and 35%-50% achieved MDA at Week 100.
Conclusion: Patients with active PsA receiving guselkumab demonstrated durable achievement of stringent endpoints associated with disease control across key PsA domains and PROs, regardless of baseline characteristics. Key Points • Among biologic-naïve patients with highly active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), efficacy of guselkumab across stringent disease endpoints and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) at Week 24 was consistent regardless of baseline demographics and disease characteristics. • Within guselkumab-randomized PsA patient subgroups, major improvements in joint disease activity, complete skin clearance, dactylitis/enthesitis resolution, clinically meaningful improvements in PROs, and achievement of low overall disease activity were maintained through Week 100. • Durable stringent endpoint achievement indicating disease control was observed with guselkumab, regardless of baseline patient or disease characteristics.
Keywords: Disease control; Domain; Guselkumab; Patient-reported outcome; Psoriatic arthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Linde L, Ornbjerg LM, Georgiadis S et al (2023) Predictors of DAPSA28 remission in patients with psoriatic arthritis initiating a first TNF-inhibitor: results from 13 European registries. Rheumatology (Oxford) 63:751–764. 10.1093/rheumatology/kead284 10.1093/rheumatology/kead284 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

