Global, regional, and national burden and trends of migraine among women of childbearing age from 1990 to 2021: insights from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
- PMID: 38844846
- PMCID: PMC11157953
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-024-01798-z
Global, regional, and national burden and trends of migraine among women of childbearing age from 1990 to 2021: insights from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Abstract
Background: Migraine, a neurological disorder with a significant female predilection, is the leading cause of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) in women of childbearing age (WCBA). There is currently a lack of comprehensive literature analysis on the overall global burden and changing trends of migraines in WCBA.
Methods: This study extracted three main indicators, including prevalence, incidence, and DALYs, related to migraine in WCBA from the Global Burden of Disease(GBD) database from 1990 to 2021. Our study presented point estimates with 95% uncertainty intervals (UIs). It evaluated the changing trends in the burden of migraine in WCBA using the estimated annual percentage change (EAPC) and percentage change.
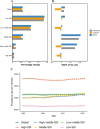
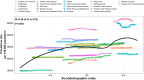
Results: In 2021, the global prevalence, incidence, and DALYs cases of migraine among WCBA were 493.94 million, 33.33 million, and 18.25 million, respectively, with percentage changes of 48%, 43%, and 47% compared to 1990. Over the past 32 years, global prevalence rates and DALYs rates globally have increased, with an EAPC of 0.03 (95% UI: 0.02 to 0.05) and 0.04 (95% UI: 0.03 to 0.05), while incidence rates have decreased with an EAPC of -0.07 (95% UI: -0.08 to -0.05). Among the 5 Socio-Demographic Index (SDI) regions, in 2021, the middle SDI region recorded the highest cases of prevalence, incidence, and DALYs of migraine among WCBA, estimated at 157.1 million, 10.56 million, and 5.81 million, respectively, approximately one-third of the global total. In terms of age, in 2021, the global incidence cases for the age group 15-19 years were 5942.5 thousand, with an incidence rate per 100,000 population of 1957.02, the highest among all age groups. The total number of migraine cases and incidence rate among WCBA show an increasing trend with age, particularly in the 45-49 age group.
Conclusions: Overall, the burden of migraine among WCBA has significantly increased globally over the past 32 years, particularly within the middle SDI and the 45-49 age group. Research findings emphasize the importance of customized interventions aimed at addressing the issue of migraines in WCBA, thus contributing to the attainment of Sustainable Development Goal 3 set by the World Health Organization.
Keywords: DALYs; Disease burden; GBD 2021; Migraine; WCBA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

