New evidence: Metformin unsuitable as routine adjuvant for breast cancer: a drug-target mendelian randomization analysis
- PMID: 38844880
- PMCID: PMC11155042
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12453-w
New evidence: Metformin unsuitable as routine adjuvant for breast cancer: a drug-target mendelian randomization analysis
Abstract
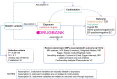
Purpose: The potential efficacy of metformin in breast cancer (BC) has been hotly discussed but never conclusive. This genetics-based study aimed to evaluate the relationships between metformin targets and BC risk.
Methods: Metformin targets from DrugBank and genome-wide association study (GWAS) data from IEU OpenGWAS and FinnGen were used to investigate the breast cancer (BC)-metformin causal link with various Mendelian Randomization (MR) methods (e.g., inverse-variance-weighting). The genetic association between type 2 diabetes (T2D) and the drug target of metformin was also analyzed as a positive control. Sensitivity and pleiotropic tests ensured reliability.
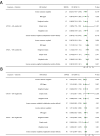
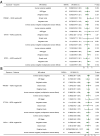
Results: The primary targets of metformin are PRKAB1, ETFDH and GPD1L. We found a causal association between PRKAB1 and T2D (odds ratio [OR] 0.959, P = 0.002), but no causal relationship was observed between metformin targets and overall BC risk (PRKAB1: OR 0.990, P = 0.530; ETFDH: OR 0.986, P = 0.592; GPD1L: OR 1.002, P = 0.806). A noteworthy causal relationship was observed between ETFDH and estrogen receptor (ER)-positive BC (OR 0.867, P = 0.018), and between GPD1L and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative BC (OR 0.966, P = 0.040). Other group analyses did not yield positive results.
Conclusion: The star target of metformin, PRKAB1, does not exhibit a substantial causal association with the risk of BC. Conversely, metformin, acting as an inhibitor of ETFDH and GPD1L, may potentially elevate the likelihood of developing ER-positive BC and HER2-negative BC. Consequently, it is not advisable to employ metformin as a standard supplementary therapy for BC patients without T2D.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Causal relationship; Drug-target mendelian randomization; Metformin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2021, 71(1). - PubMed
-
- Wolf I, Sadetzki S, Catane R, Karasik A, Kaufman B. Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer. Ztschrift Für Ernhrungswissenschaftjournal Nutritional Encessupplementa. 2005;14(2):Suppl.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

