LKB1 biology: assessing the therapeutic relevancy of LKB1 inhibitors
- PMID: 38844908
- PMCID: PMC11155146
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01689-5
LKB1 biology: assessing the therapeutic relevancy of LKB1 inhibitors
Abstract
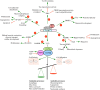
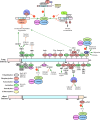
Liver Kinase B1 (LKB1), encoded by Serine-Threonine Kinase 11 (STK11), is a master kinase that regulates cell migration, polarity, proliferation, and metabolism through downstream adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and AMPK-related kinase signalling. Since genetic screens identified STK11 mutations in Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome, STK11 mutants have been implicated in tumourigenesis labelling it as a tumour suppressor. In support of this, several compounds reduce tumour burden through upregulating LKB1 signalling, and LKB1-AMPK agonists are cytotoxic to tumour cells. However, in certain contexts, its role in cancer is paradoxical as LKB1 promotes tumour cell survival by mediating resistance against metabolic and oxidative stressors. LKB1 deficiency has also enhanced the selectivity and cytotoxicity of several cancer therapies. Taken together, there is a need to develop LKB1-specific pharmacological compounds, but prior to developing LKB1 inhibitors, further work is needed to understand LKB1 activity and regulation. However, investigating LKB1 activity is strenuous as cell/tissue type, mutations to the LKB1 signalling pathway, STE-20-related kinase adaptor protein (STRAD) binding, Mouse protein 25-STRAD binding, splicing variants, nucleocytoplasmic shuttling, post-translational modifications, and kinase conformation impact the functional status of LKB1. For these reasons, guidelines to standardize experimental strategies to study LKB1 activity, associate proteins, spliced isoforms, post-translational modifications, and regulation are of upmost importance to the development of LKB1-specific therapies. Therefore, to assess the therapeutic relevancy of LKB1 inhibitors, this review summarizes the importance of LKB1 in cell physiology, highlights contributors to LKB1 activation, and outlines the benefits and risks associated with targeting LKB1.
Keywords: Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK); Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase-related Kinases (ARKs); Autophosphorylation; Drug Discovery; LKB1 Inhibitors; Liver Kinase B1 (LKB1); Mouse Protein 25 (MO25); Post-translational Modifications; STE-20-related Kinase Adaptor Protein (STRAD); Tumour Suppressor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolic stress induces a double-positive feedback loop between AMPK and SQSTM1/p62 conferring dual activation of AMPK and NFE2L2/NRF2 to synergize antioxidant defense.Autophagy. 2024 Nov;20(11):2490-2510. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2374692. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 38953310 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into targeting LKB1 in tumorigenesis.Genes Dis. 2024 Aug 28;12(2):101402. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101402. eCollection 2025 Mar. Genes Dis. 2024. PMID: 39735555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning developed LKB1-AMPK signaling related signature for prognosis and drug sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20738. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08583-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594698 Free PMC article.
-
LKB1 regulates ILC3 postnatal development and effector function through metabolic programming.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1587256. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1587256. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40539052 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Liver kinase B1 expression is associated with improved prognosis and tumor immune microenvironment features in small cell lung cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 4;15:1552506. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1552506. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40255421 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on AMPK in the pathogenesis and treatment of MASLD.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 11;16:1558041. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1558041. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40134423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear functional role of metabolic enzymes and related metabolites: Focus on gene expression regulation.Mol Metab. 2025 Aug 7;100:102233. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2025.102233. Online ahead of print. Mol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40780444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Procyanidin B2-induced LKB1-AMPK activation mitigates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through inhibition of mTOR signaling.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2025 Sep 1;29(5):659-667. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.25.108. Epub 2025 Jul 24. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40701843 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting LKB1/STK11-mutant cancer: distinct metabolism, microenvironment, and therapeutic resistance.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2025 Aug;46(8):722-737. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2025.06.008. Epub 2025 Jul 22. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40701847 Review.
References
-
- Hemminki A, et al. A serine/threonine kinase gene defective in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Nat Genet. 1998;391:184–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

