Integrin αVβ1-activated PYK2 promotes the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the STAT3-VGF axis
- PMID: 38844957
- PMCID: PMC11157819
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01639-1
Integrin αVβ1-activated PYK2 promotes the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the STAT3-VGF axis
Abstract
Background: Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 80-85% of all lung cancer and is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. Although various treatment strategies have been introduced, the 5-year survival rate of patients with NSCLC is only 20-30%. Thus, it remains necessary to study the pathogenesis of NSCLC and develop new therapeutic drugs. Notably, PYK2 has been implicated in the progression of many tumors, including NSCLC, but its detailed mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the mechanisms through which PYK2 promotes NSCLC progression.
Methods: The mRNA and protein levels of various molecules were measured using qRT-PCR, western blot (WB), and immunohistochemistry (IHC), respectively. We established stable PYK2 knockdown and overexpression cell lines, and CCK-8, EdU, and clonogenic assays; wound healing, transwell migration, and Matrigel invasion assays; and flow cytometry were employed to assess the phenotypes of tumor cells. Protein interactions were evaluated with co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP), immunofluorescence (IF)-based colocalization, and nucleocytoplasmic separation assays. RNA sequencing was performed to explore the transcriptional regulation mediated by PYK2. Secreted VGF levels were examined using ELISA. Dual-luciferase reporter system was used to detect transcriptional regulation site. PF4618433 (PYK2 inhibitor) and Stattic (STAT3 inhibitor) were used for rescue experiments. A public database was mined to analyze the effect of these molecules on NSCLC prognosis. To investigate the role of PYK2 in vivo, mouse xenograft models of lung carcinoma were established and examined.
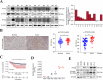
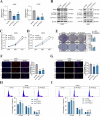
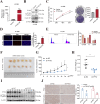
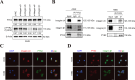
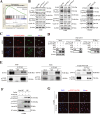
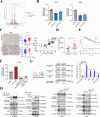
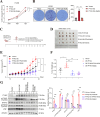
Results: The protein level of PYK2 was higher in human NSCLC tumors than in the adjacent normal tissue, and higher PYK2 expression was associated with poorer prognosis. PYK2 knockdown inhibited the proliferation and motility of tumor cells and caused G1-S arrest and cyclinD1 downregulation in A549 and H460 cells. Meanwhile, PYK2 overexpression had the opposite effect in H1299 cells. The siRNA-induced inhibition of integrins alpha V and beta 1 led to the downregulation of p-PYK2(Tyr402). Activated PYK2 could bind to STAT3 and enhance its phosphorylation at Tyr705, regulating the nuclear accumulation of p-STAT3(Tyr705). This further promoted the expression of VGF, as confirmed by RNA sequencing in a PYK2-overexpressing H1299 cell line and validated by rescue experiments. Two sites in promoter region of VGF gene were confirmed as binding sites of STAT3 by Dual-luciferase assay. Data from the TGCA database showed that VGF was related to the poor prognosis of NSCLC. IHC revealed higher p-PYK2(Tyr402) and VGF expression in lung tumors than in adjacent normal tissues. Moreover, both proteins showed higher levels in advanced TNM stages than earlier ones. A positive linear correlation existed between the IHC score of p-PYK2(Tyr402) and VGF. Knockdown of VGF inhibited tumor progression and reversed the tumor promoting effect of PYK2 overexpression in NSCLC cells. Finally, the mouse model exhibited enhanced tumor growth when PYK2 was overexpressed, while the inhibitors PF4618433 and Stattic could attenuate this effect.
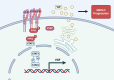
Conclusions: The Integrin αVβ1-PYK2-STAT3-VGF axis promotes NSCLC development, and the PYK2 inhibitor PF4618433 and STAT3 inhibitor Stattic can reverse the pro-tumorigenic effect of high PYK2 expression in mouse models. Our findings provide insights into NSCLC progression and could guide potential therapeutic strategies against NSCLC with high PYK2 expression levels.
Keywords: Integrin αVβ1; Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC); Nuclear accumulation of p-STAT3(Tyr705); PYK2; VGF.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease. Cancer C, Kocarnik JM, Compton K, Dean FE, Fu W, Gaw BL, Harvey JD, Henrikson HJ, Lu D, Pennini A, et al. Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life years for 29 Cancer groups from 2010 to 2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of Disease Study 2019. JAMA Oncol. 2022;8(3):420–44. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.6987. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SKY2022044/Suzhou New Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment Technologies and Public Health
- 82073213/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- GSWS2020016/The Suzhou Gusu Medical Youth Talent
- 2022-3-25-162/The 6th"333 High-level Talents Training Project" of Jiangsu Province
- ZDXK202201/Jiangsu Provincial Medical Key Discipline
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

