POLR1D silencing suppresses lung cancer cells proliferation and migration via inhibition of PI3K-Akt pathway
- PMID: 38844975
- PMCID: PMC11155163
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-024-02791-y
POLR1D silencing suppresses lung cancer cells proliferation and migration via inhibition of PI3K-Akt pathway
Abstract
Aim: The most common type of cancer that leads to death worldwide is lung cancer. Despite significant surgery and chemotherapy improvements, lung cancer patient's survival rate is still poor. The RNA polymerase I subunit D (POLR1D) gene can induce various cancers. A current study reported that POLR1D plays a vital role in cancer prognosis. However, its biological function in the development of lung cancer remains unclear.
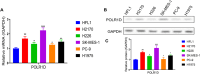
Methods: Reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) measured the relative POLR1D protein expression level in lung cancer cell lines. Lung cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were analyzed by performing cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), and transwell. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/serine-threonine kinase (PI3K/AKT) signaling pathway-related protein expressions were examined by Western blotting assay.
Results: POLR1D protein expression was elevated in lung cancer. Lung cancer cell loss-of-function tests showed that POLR1D silencing could attenuate cell viability both in SK-MES-1 and in H2170 cells. Furthermore, silencing POLR1D inhibited SK-MES-1 and H2170 cells proliferation, migration, and invasion. Moreover, SK-MES-1 and H2170 cells' migration and invasion capacity were potentially suppressed by the knockdown of POLR1D. The progression of multiple cancers has been implicated in the PI3K/AKT pathway. Here, we observed that POLR1D silencing suppressed lung cancer progression by inhibition of the PI3K-Akt pathway.
Conclusions: The study speculated that POLR1D might provide a new potential therapeutic possibility for treating lung cancer patients via targeting PI3K/AKT.
Keywords: AKT; Cell proliferation; Lung cancer; PI3K; POLR1D.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

