Impact of extramedullary multiple myeloma on outcomes with idecabtagene vicleucel
- PMID: 38845015
- PMCID: PMC11157748
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-024-01555-4
Impact of extramedullary multiple myeloma on outcomes with idecabtagene vicleucel
Abstract
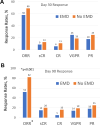
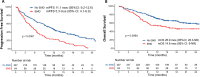
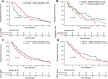
Idecabtagene vicleucel (Ide-cel) has demonstrated excellent efficacy and durable responses in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). However, the outcomes with ide-cel in patients with extramedullary disease (EMD) remain incompletely characterized. We included patients with RRMM treated with ide-cel between May 2021 and April 2023 across 11 US academic institutions. Visceral or soft tissue lesions non-contiguous from bone was classified as EMD. Time-to-event analyses were performed from date of ide-cel infusion. Among 351 patients, 84 (24%) had EMD prior to infusion. The median follow-up from ide-cel infusion was 18.2 months (95% CI: 17-19.3). The day 90 overall response rates (ORR) were 52% vs. 82% for the EMD and non-EMD cohorts, respectively (p < 0.001). The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 5.3 months (95% CI: 4.1-6.9) for the EMD cohort vs. 11.1 months (95% CI: 9.2-12.6; p < 0.0001) for the non-EMD cohort. In a multivariable analysis, EMD was an independent predictor of inferior PFS [hazard ratio 1.5 (1.1-2.2), p = 0.02]. The median overall survival was 14.8 months [95% CI: 9-Not reached (NR)] vs. 26.9 months (26.3 vs. NR, p = 0.006) for the EMD and non-EMD cohorts, respectively. Extramedullary disease represents an independent predictor of inferior day 90 ORR and PFS among patients treated with ide-cel.
Keywords: BCMA CAR-T; Ide-cel; Immunotherapy; Radiation; Relapsed/refractory myeloma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.Z., O.P, R.G., D.D. G.K, M.H, P.F, C.W.A.L-C.: no relevant disclosures. S.S.: Consulting or advisory role for Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Legend, Magenta Therapeutics, Sanofi, Pfizer, Takeda, Kite, Abbvie and Regeneron; Research funding from Janssen, Magenta Therapeutics, Allogene Therapeutics, Novartis and Bristol-Myers Squibb; L.S.: Consulting or Advisory role for Janssen Oncology; O.C.P.: Consulting or Advisory role for BMS/Celgene/Juno, Legend Biotech; A.A.: Consulting or Advisory role for BMS, Karyopharm, Research funding from Abbvie, Adaptive biotechnologies; J.A.D.: consultancy for Janssen; H.H.; Consulting or Advisory role for Sanofi, BMS/Celgene, Janssen; speaker’s bureau: Janssen, Karyopharm, Amgen; D.S.: Consulting or Advisory role for Sanofi, GSK, BMS/Celgene, Janssen, Abbvie, Pfizer, Arcellx, BiolineRx, Astrazeneca, research funding from Pfizer; L.D.A. Jr: consulting or advisory board role for Janssen, Celgene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Amgen, GlaxoSmithKline, AbbVie, BeiGene, Cellectar, Sanofi, Karyopharm, Oncopeptides, and Prothena. J.M: Honoraria: Kite, a Gilead company, AlloVir, Magenta Therapeutics, Nektar, Sana Biotechnology; Consulting or Advisory Role: Kite, a Gilead company, Juno Therapeutics, AlloVir, Magenta Therapeutics, EcoR1 Capital, CRISPR therapeutics; Speakers’ Bureau: Kite/Gilead; Research Funding: Novartis (Inst), Fresenius Biotech (Inst), Astellas Pharma (Inst), Bellicum Pharmaceuticals (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Gamida Cell (Inst), Pluristem Therapeutics (Inst), Kite, a Gilead company (Inst), AlloVir (Inst); Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Kite, a Gilead company; A.R.: consultant for Sanofi, BMS, Janssen, and Adaptive. C.R. is a consultant for Janssen, BMS, Takeda, Sanofi, and Artiva; C.L.F: horonoraria and consulting- Bristol Myers Squibb, Seattle Genetics, Celgene, AbbVie, Sanofi, Incyte, Amgen, ONK Therapeutics & Janssen; and research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, and Roche/Genentech; F.L.L.: Scientific Advisory Role/Consulting Fees: A2, Allogene, Amgen, Bluebird Bio, BMS, Calibr, Caribou, Cowen, EcoR1, Gerson Lehrman Group (GLG), Iovance, Kite Pharma, Janssen, Legend Biotech, Novartis, Sana, Umoja, Pfizer; Data Safety Monitoring Board: Data and Safety Monitoring Board for the NCI Safety Oversight CAR T-cell Therapies Committee. Research Contracts or Grants to my Institution for Service: Kite Pharma (Institutional), Allogene (Institutional), CERo Therapeutics (Institutional), Novartis (Institutional), BlueBird Bio (Institutional), 2SeventyBio (Institutional), BMS (Institutional), National Cancer Institute (R01CA244328 MPI: Locke; P30CA076292 PI: Cleveland), Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Scholar in Clinical Research (PI: Locke); Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: Several patents held by the institution in my name (unlicensed) in the field of cellular immunotherapy; Education or Editorial Activity: Aptitude Health, ASH, BioPharma Communications CARE Education, Clinical Care Options Oncology, Imedex, Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer S.R.: Honoraria: BMs, Jansssen; Consulting or Advisory Role: Genentech; Research Funding: Janssen, C4 therapeutics, Gracell, Heidelberg Pharma; J.K.: Consulting or Advisory Role: Janssen Oncology; Honoraria: GPCR therapeutics; Y.L.: Consulting or Advisory role: Kite/Gilead, BMS, Vineti, Janssen Oncology, Pfizer; Sanofi, NexImmune, Caribou biosciences, Regeneron, Genentech, Fosun Kite, Chimeric Therapeutics, Adicet Bio, Nektar; Research Funding: Janssen Oncoloyg, BMS, Merck, Takeda, Boston Scientific, Kite/Gilead, Bluebird Bio; K.K.P.: Consulting or Advisory Role: Celgene, BMS, Janssen, Pfizer, Arcellx, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Merck, Cellectis, Caribou Biosciences, Takeda, Abbvie, Travel, Accomodation, Expenses: BMS; Research funding: Celgene/BMs, Takeda, Janssen, Cellectis, Nektar, Abbvie/Genentech, Precision Biosciences, Allogene Therapeutics; S.K.: Consulting or Advisory Role: Takeda, Janssen Oncology, Genentech/Rocher, Abbvie, BMS/Celgene, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, K36 Therapeutics; travel, accomodation and expenses: Abbvie, pfizer; Research funding: Takeda, Abbvie, Novartis, Sanofi, Janssen Oncology, MedImmune, Roche/Genentech, CARsgen Therapeutics, Allogene Therapeutics, GSK, Regeneron, BMS/Celgene; D.K.H.: Research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Karyopharm, and Adaptive Biotech; Consulting or advisory role for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Pfizer, and Karyopharm. D.K.H is also supported by the Pentecost Family Myeloma Research Center.
Figures
References
-
- Usmani SZ, Heuck C, Mitchell A, Szymonifka J, Nair B, Hoering A, et al. Extramedullary disease portends poor prognosis in multiple myeloma and is over-represented in high-risk disease even in the era of novel agents. Haematologica. 2012;97(11):1761–7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.065698. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

