The complex roles of m 6 A modifications in neural stem cell proliferation, differentiation, and self-renewal and implications for memory and neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 38845217
- PMCID: PMC11688559
- DOI: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01872
The complex roles of m 6 A modifications in neural stem cell proliferation, differentiation, and self-renewal and implications for memory and neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
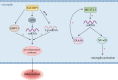
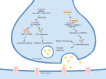
N6-methyladenosine (m 6 A), the most prevalent and conserved RNA modification in eukaryotic cells, profoundly influences virtually all aspects of mRNA metabolism. mRNA plays crucial roles in neural stem cell genesis and neural regeneration, where it is highly concentrated and actively involved in these processes. Changes in m 6 A modification levels and the expression levels of related enzymatic proteins can lead to neurological dysfunction and contribute to the development of neurological diseases. Furthermore, the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells, as well as nerve regeneration, are intimately linked to memory function and neurodegenerative diseases. This paper presents a comprehensive review of the roles of m 6 A in neural stem cell proliferation, differentiation, and self-renewal, as well as its implications in memory and neurodegenerative diseases. m 6 A has demonstrated divergent effects on the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells. These observed contradictions may arise from the time-specific nature of m 6 A and its differential impact on neural stem cells across various stages of development. Similarly, the diverse effects of m 6 A on distinct types of memory could be attributed to the involvement of specific brain regions in memory formation and recall. Inconsistencies in m 6 A levels across different models of neurodegenerative disease, particularly Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, suggest that these disparities are linked to variations in the affected brain regions. Notably, the opposing changes in m 6 A levels observed in Parkinson's disease models exposed to manganese compared to normal Parkinson's disease models further underscore the complexity of m 6 A's role in neurodegenerative processes. The roles of m 6 A in neural stem cell proliferation, differentiation, and self-renewal, and its implications in memory and neurodegenerative diseases, appear contradictory. These inconsistencies may be attributed to the time-specific nature of m 6 A and its varying effects on distinct brain regions and in different environments.
Copyright © 2025 Copyright: © 2025 Neural Regeneration Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Progression of N6-methyladenosine Study and Its Role in Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 25;23(11):5922. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115922. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of m 6A modification in central nervous system function and disease.Yi Chuan. 2020 Dec 17;42(12):1156-1167. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-233. Yi Chuan. 2020. PMID: 33509780 Review.
-
Adult neurogenesis and neurodegenerative diseases: A systems biology perspective.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017 Jan;174(1):93-112. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32429. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017. PMID: 26879907 Free PMC article.
-
Neural stem cells could serve as a therapeutic material for age-related neurodegenerative diseases.World J Stem Cells. 2015 Mar 26;7(2):502-11. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.502. World J Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 25815135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The Roles of N6-Methyladenosine Modification and Its Regulators in Male Reproduction].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 20;55(3):527-534. doi: 10.12182/20240560103. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38948273 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Identification of ferroptosis-related gene signatures in temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis.Front Neurosci. 2025 Apr 2;19:1530182. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1530182. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40242460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilo F, Zhang F, Sancho A, Fidalgo M, Di Cecilia S, Vashisht A, Lee DF, Chen CH, Rengasamy M, Andino B, Jahouh F, Roman A, Krig SR, Wang R, Zhang W, Wohlschlegel JA, Wang J, Walsh MJ. Coordination of m(6)A mRNA methylation and gene transcription by ZFP217 regulates pluripotency and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17:689–704. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avgustinova A, Benitah SA. Epigenetic control of adult stem cell function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17:643–658. - PubMed
-
- Boles NC, Temple S. Epimetronomics: m6A marks the tempo of corticogenesis. Neuron. 2017;96:718–720. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Zhuang Y, Chen J, Xu W, Shou Y, Huang X, Shu Q, Li X. Dynamic effects of Fto in regulating the proliferation and differentiation of adult neural stem cells of mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2020;29:727–735. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

