Recent advances in understanding the mechanisms in skeletal muscle of interaction between exercise and frontline antihyperglycemic drugs
- PMID: 38845596
- PMCID: PMC11157199
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.16093
Recent advances in understanding the mechanisms in skeletal muscle of interaction between exercise and frontline antihyperglycemic drugs
Abstract
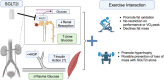
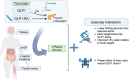
Regular exercise and antihyperglycemic drugs are front-line treatments for type-2 diabetes and related metabolic disorders. Leading drugs are metformin, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists. Each class has strong individual efficacy to treat hyperglycemia, yet the combination with exercise can yield varied results, some of which include blunting of expected metabolic benefits. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance contributes to the development of type-2 diabetes while improvements in skeletal muscle insulin signaling are among key adaptations to exercise training. The current review identifies recent advances into the mechanisms, with an emphasis on skeletal muscle, of the interaction between exercise and these common antihyperglycemic drugs. The review is written toward researchers and thus highlights specific gaps in knowledge and considerations for future study directions.
Keywords: aerobic; glucagon‐like peptide 1 receptor agonist; metformin; mitochondria; resistance; sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor.
© 2024 The Author(s). Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Blundell, J. , Finlayson, G. , Axelsen, M. , Flint, A. , Gibbons, C. , Kvist, T. , & Hjerpsted, J. B. (2017). Effects of once‐weekly semaglutide on appetite, energy intake, control of eating, food preference and body weight in subjects with obesity. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism, 19, 1242–1251. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bouchi, R. , Sonoda, N. , Itoh, J. , Ono, Y. , Fukuda, T. , Takeuchi, T. , Kishimoto, J. , Yamada, T. , & Ogawa, Y. (2021). Effects of intensive exercise combined with dapagliflozin on body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Endocrine Journal, 68, 329–343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

