C1GALT1 induces the carcinogenesis of thyroid cancer through regulation by miR-141-3p and GLUT1
- PMID: 38845937
- PMCID: PMC11153184
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31778
C1GALT1 induces the carcinogenesis of thyroid cancer through regulation by miR-141-3p and GLUT1
Abstract
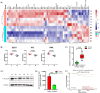
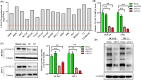
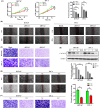
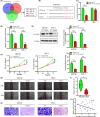
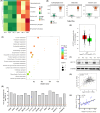
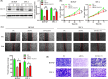
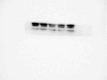
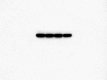
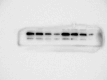
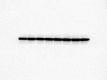
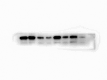
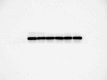
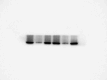
Core 1 β 1,3-galactosyltransferase 1 (C1GALT1) acts as an important glycosyltransferase in the occurrence and development of tumor glycosylation. However, the regulatory mechanisms of C1GALT1 in thyroid cancer (TC) is still unclear. In this study, we discovered that the expression level of C1GALT1 was significantly increased in thyroid adenocarcinoma tissues and cell lines (p < 0.01). Meanwhile, gene silencing of C1GALT1 inhibited the proliferation (CCK-8 assay), migration (wound healing), and invasion (Transwell) of TC cells (p < 0.05). Further investigation indicated that miR-141-3p had a negative correlation with C1GALT1 and suppressed cancer carcinogenesis in TC cells. Moreover, we first found that glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) was a downstream element of C1GALT1 and was positively correlated with C1GALT1 levels in TC. The GLUT1 could reverse the inhibitory effects of siRNA C1GALT1 on cell development (p < 0.05). These data suggest that the miR-141-3p/C1GALT1/GLUT1 axis plays an essential role during TC progression and may be a probable biomarker or therapeutic target for thyroid cancer patients.
Keywords: C1GALT1; Carcinogenesis; GLUT1; Metastasis; Thyroid cancer; miR-141-3p.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

