Biometric factors associated with the postoperative visual performance of a multifocal intraocular lens
- PMID: 38845945
- PMCID: PMC11154599
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31867
Biometric factors associated with the postoperative visual performance of a multifocal intraocular lens
Abstract
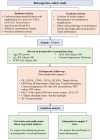
Purpose: To identify the biometric factors associated with postoperative visual performance after uneventful phacoemulsification with multifocal intraocular lens (MIOL) implantation.
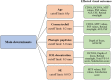
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, 72 eyes of 72 patients implanted with the HumanOptics Diff-aAY MIOL were included. Preoperative examination data including the white-to-white distance (WTW), anterior chamber depth (ACD), axial length and corneal astigmatism were gathered through the electronic medical records. One month postoperatively, the pupil parameters, corneal aberrations, corneal astigmatism, IOL tilts and IOL decentrations were measured using an OPD-Scan III aberrometer. Postoperative visual performance parameters were recorded as the visual acuity, depth of focus, modulation transfer function (MTF) and point spread function (PSF) values, area under log contrast sensitivity function (AULCSF), retinal straylight and visual function questionnaire scores. Univariate and multivariate linear regression analyses were then performed to evaluate the associations between the potential biometric factors and postoperative visual outcomes.
Results: Younger age predicted greater MTF and PSF values, better AULCSF and better retinal straylight (P < 0.05). A lower corneal trefoil predicted better MTF and PSF values (P < 0.05). Smaller IOL decentration predicted better distance-corrected near visual acuity, greater AULCSF and better retinal straylight (P < 0.05). A less negative spherical equivalent (SE) predicted better MTF values (P = 0.017), while a more negative SE predicted better Visual Function Index-14 (VF-14) questionnaire scores and satisfaction scores (P < 0.05). A higher IOL power predicted better best corrected distance visual acuity (P = 0.005). Lower preoperative corneal astigmatism predicted greater MTF values (P = 0.020). Lower postoperative corneal astigmatism, smaller corneal high-order aberrations (HOAs), smaller photopic pupil size, larger WTW and deeper ACD predicted a better AULCSF (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: IOL decentration, IOL power, age, preoperative and postoperative corneal astigmatism, SE, photopic pupil size, corneal trefoil, WTW, ACD and corneal HOAs were significantly associated with postoperative visual performance. These findings might aid in patient selection prior to MIOL implantation.
Keywords: Biometric factors; Multifocal intraocular lens; Multivariate linear regression analyses; Visual performance.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Steinert R.F. Visual outcomes with multifocal intraocular lenses. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2000;11(1):12–21. - PubMed
-
- Rampat R., Gatinel D. Multifocal and extended depth-of-focus intraocular lenses in 2020. Ophthalmology. 2021;128(11) - PubMed
-
- Vega F., Alba-Bueno F., Millán M.S., Varón C., Gil M.A., Buil J.A. Halo and through-focus performance of four diffractive multifocal intraocular lenses. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2015;56(6) - PubMed
-
- Fu Y., Kou J., Chen D., Wang D., Zhao Y., Hu M., Lin X., Dai Q., Li J., Zhao Y. Influence of angle kappa and angle alpha on visual quality after implantation of multifocal intraocular lenses. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2019;45(9):1258–1264. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

