Efficacy and safety of intravitreal injection of conbercept for moderate to severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 38846145
- PMCID: PMC11153662
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1394358
Efficacy and safety of intravitreal injection of conbercept for moderate to severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of intravitreal injection of conbercept (IVC) in treating moderate to severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR), with or without accompanying diabetic macular edema.
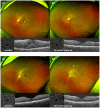
Methods: In this longitudinal retrospective study, 35 patients (50 eyes) with moderate to severe NPDR and Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scale (DRSS) scores between 43 and 53 were treated at the Department of Ophthalmology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, from October 2018 to January 2023. Treatment protocol included three monthly IVC injections followed by a pro re nata (PRN) regimen over a two-year follow-up period. Outcome measures were best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), intraocular pressure, central macular thickness (CMT), extent of hard exudate (HE), and changes in DRSS scores. DRSS scores before and after treatment were analyzed using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Both systemic and ocular adverse events were meticulously documented to ascertain safety.
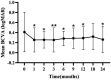
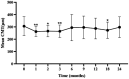
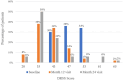
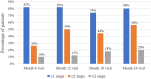
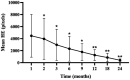
Results: From baseline to the final follow-up, the mean BCVA improved from 0.41 ± 0.39 to 0.23 ± 0.20 logMAR (p<0.05). The mean CMT decreased from 306.22 ± 77.40 to 297.97 ± 88.15 μm (p = 0.385). At 24 months, DRSS scores improved by ≥1 stage in 40 eyes (80%), ≥ 2 stages in 28 eyes (56%), ≥3 stages in 10 eyes (20%), and remained stable in 6 eyes (12%). The DRSS scores at each follow-up interval demonstrated statistically significant improvement from baseline (p<0.05). In 15 of 27 eyes (55.56%) with diabetic macular edema (DME), there was a significant reduction in the mean area of HE from baseline (p<0.05). No serious systemic adverse events were observed.
Conclusion: IVC is an effective and safe treatment for moderate to severe NPDR, demonstrating significant improvements in DRSS scores.
Keywords: Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scale; VEGF – vascular endothelial growth factor; conbercept; diabetic macular edema; moderate to severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Copyright © 2024 Shen, Zheng, Gao, Li, Dai, Yang, Zhang, Li, Hu and Yuan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Intravitreal Aflibercept for the Treatment of Severe Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: Results From the PANORAMA Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021 Sep 1;139(9):946-955. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2021.2809. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34351414 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
One-year outcomes of novel VEGF decoy receptor therapy with intravitreal conbercept in diabetic retinopathy-induced macular edema.Mol Vis. 2019 Oct 21;25:636-644. eCollection 2019. Mol Vis. 2019. PMID: 31700228 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of less aggressive treatment on diabetic retinopathy severity scale scores: analyses of the RIDE and RISE open-label extension.BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2022 Jul;7(1):e001007. doi: 10.1136/bmjophth-2022-001007. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36161830 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Update on Management of Non-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy without Diabetic Macular Edema; Is There a Paradigm Shift?J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2022 Jan 21;17(1):108-117. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v17i1.10175. eCollection 2022 Jan-Mar. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2022. PMID: 35194501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intravitreal Ranibizumab Alone or in Combination with Calcium Dobesilate for the Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema in Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Patients: 12-Month Outcomes of a Retrospective Study.Int J Clin Pract. 2022 Oct 20;2022:6725225. doi: 10.1155/2022/6725225. eCollection 2022. Int J Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 36340967 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancement of retinal Müller glia's phagocytic activity against hard exudates by conbercept via activation of PPARγ-CD36 axis in diabetic retinopathy.Int J Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 18;18(7):1252-1261. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2025.07.07. eCollection 2025. Int J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40688793 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous-humor biomarkers and real-world efficacy of conbercept for diabetic macular edema: a prospective study in elderly patients.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 7;16:1632878. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1632878. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40692595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wadhwani M, Bali S, Bhartiya S, Mahabir M, Upadhaya A, Dada T, et al. . Long term effect of panretinal photocoagulation on retinal nerve fiber layer parameters in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Oman J Ophthalmol. (2019) 12:181–5. doi: 10.4103/ojo.OJO_39_2018, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

