Zinc-Containing Over-The-Counter Product Causing Sideroblastic Anemia and Neutropenia
- PMID: 38846187
- PMCID: PMC11155223
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.59796
Zinc-Containing Over-The-Counter Product Causing Sideroblastic Anemia and Neutropenia
Abstract
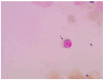
Sideroblastic anemia is characterized by anemia, granulocytopenia, and bone marrow findings of vacuolated precursors and ringed sideroblasts. Zinc-induced copper deficiency can present as sideroblastic anemia and neutropenia. We report the case of a previously healthy 74-year-old female who presented with newly discovered sideroblastic anemia as a result of an over-the-counter oral vitamin and mineral supplement. Serum analysis revealed increased zinc levels, decreased copper levels, and a decrease in ceruloplasmin. Bone marrow evaluation revealed ringed sideroblasts and cytoplasmic vacuolization in myeloid precursors. She demonstrated improvement in her hematologic profile with discontinuation of the over-the-counter product and administration of oral copper supplementation. This case highlights the importance of sideroblastic anemia recognition and careful medication review, including over-the-counter supplements.
Keywords: copper; neutropenia; sideroblastic anemia; zinc; zinc-induced hypocupremia.
Copyright © 2024, Stagg et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Sideroblastic anemia secondary to zinc toxicity. Sheqwara J, Alkhatib Y. Blood. 2013;122:311. - PubMed
-
- Zinc-induced sideroblastic anemia: report of a case, review of the literature, and description of the hematologic syndrome. Fiske DN, McCoy HE 3rd, Kitchens CS. Am J Hematol. 1994;46:147–150. - PubMed
-
- Trace metals in hematopoiesis. Deur CJ, Stone MJ, Frenkel EP. Am J Hematol. 1981;11:309–331. - PubMed
-
- Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine. Washington: National Academies Press; 1981. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
