Clinically used drug arsenic trioxide targets XIAP and overcomes apoptosis resistance in an organoid-based preclinical cancer model
- PMID: 38846391
- PMCID: PMC11151819
- DOI: 10.1039/d4sc01294a
Clinically used drug arsenic trioxide targets XIAP and overcomes apoptosis resistance in an organoid-based preclinical cancer model
Abstract
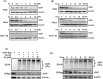
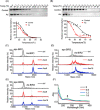
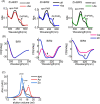
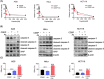
Drug resistance in tumor cells remains a persistent clinical challenge in the pursuit of effective anticancer therapy. XIAP, a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) family, suppresses apoptosis via its Baculovirus IAP Repeat (BIR) domains and is responsible for drug resistance in various human cancers. Therefore, XIAP has attracted significant attention as a potential therapeutic target. However, no XIAP inhibitor is available for clinical use to date. In this study, we surprisingly observed that arsenic trioxide (ATO) induced a rapid depletion of XIAP in different cancer cells. Mechanistic studies revealed that arsenic attacked the cysteine residues of BIR domains and directly bound to XIAP, resulting in the release of zinc ions from this protein. Arsenic-XIAP binding suppressed the normal anti-apoptosis functions of BIR domains, and led to the ubiquitination-dependent degradation of XIAP. Importantly, we further demonstrate that arsenic sensitized a variety of apoptosis-resistant cancer cells, including patient-derived colon cancer organoids, to the chemotherapy drug using cisplatin as a showcase. These findings suggest that targeting XIAP with ATO offers an attractive strategy for combating apoptosis-resistant cancers in clinical practice.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Engineering ML-IAP to produce an extraordinarily potent caspase 9 inhibitor: implications for Smac-dependent anti-apoptotic activity of ML-IAP.Biochem J. 2005 Jan 1;385(Pt 1):11-20. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041108. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15485396 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose arsenic trioxide sensitizes glucocorticoid-resistant acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells to dexamethasone via an Akt-dependent pathway.Blood. 2007 Sep 15;110(6):2084-91. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-12-060970. Epub 2007 May 30. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17537996
-
XIAP BIR domain suppresses miR-200a expression and subsequently promotes EGFR protein translation and anchorage-independent growth of bladder cancer cell.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jan 5;10(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0376-9. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28057023 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) as potential molecular targets for therapy of hematological malignancies.Curr Mol Med. 2011 Nov;11(8):633-49. doi: 10.2174/156652411797536723. Curr Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21902653 Review.
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein - a critical death resistance regulator and therapeutic target for personalized cancer therapy.Front Oncol. 2014 Jul 28;4:197. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00197. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25120954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Carboplatin combined with arsenic trioxide versus carboplatin combined with docetaxel treatment for LACC: A randomized, open-label, phase II clinical study.Open Med (Wars). 2024 Dec 12;19(1):20241106. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-1106. eCollection 2024. Open Med (Wars). 2024. PMID: 39669373 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of PANoptosis-related genes for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by machine learning and molecular subtype analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 14;14(1):24068. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76263-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39402203 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

