Mobile Technologies for Monitoring Sleep Time: A Systematic Search of App Stores in Brazil
- PMID: 38846586
- PMCID: PMC11152620
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0044-1779606
Mobile Technologies for Monitoring Sleep Time: A Systematic Search of App Stores in Brazil
Abstract
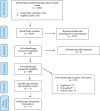
Introduction Decreased sleep time is detrimental to physical and mental health, exerting negative impacts on daily functioning and quality of life. Mobile health (mHealth) applications can be useful for improving sleep quality. Objective To perform a systematic search of mHealth applications for monitoring sleep time at Brazilian online stores and evaluate the selected applications in terms of engagement, functionality, aesthetics, and quality of information. Methods A systematic search was performed at the Google Play Store and the App Store developed or updated between 2020 and 2022. The mobile app rating scale (MARS) was used to assess their quality. The characteristics and information of these applications were presented. Data were analyzed descriptively. Results Among the 2,264 relevant mHealth apps identified, 11 were eligible for inclusion. There was one app that offered only sleep time recordings, three offered sleep recordings and educational content, three monitored sleep time with audiovisual resources, two offered sleep time recordings with a focus on monitoring snoring, and two offered sleep time monitoring with individual content customizations. The apps scored fair on MARS, with a mean of 3.5 points (standard deviation: 0.8) on a scale of 1 to 5. Most apps scored low due to poor evidence-based information, aesthetics, and engagement. Conclusion Although the use of mHealth technologies for monitoring sleep time has considerable potential for investigation, it is a relatively new, underexplored topic. Collaboration between researchers, clinical professionals, patients, and application developers is necessary for the creation of new evidence-based mHealth applications focused on Brazilian users.
Keywords: e-Health; mobile applications; public health; sleep; sleeping habits.
Brazilian Sleep Association. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Crispim C A, Zalcman I, Dáttilo Met al. Relação entre sono e obesidade: uma revisão da literatura. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab [Internet]2007Oct;51(Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab, 2007 51(7)). Available from:https://doi.org/10.1590/S0004-27302007000700004 - PubMed
-
- Crepaldi T, Carvalhais J.A contribuição da má qualidade do sono na qualidade de vida no trabalho de professores: Uma revisão[The contribution of bad sleeping quality on professors work life: A review]Brazilian Journal of Development 202061075044–75057. 10.34117/bjdv6n10-070 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

