Relationship between oral health literacy and oral health-related quality of life in patients with bladder cancer
- PMID: 38846611
- PMCID: PMC11155477
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1385443
Relationship between oral health literacy and oral health-related quality of life in patients with bladder cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Bladder cancer is one of the most important diseases that threatens oral and dental health due to its nature and side effects of chemotherapy. Therefore, the present study was conducted to investigate the relationship between oral health literacy and oral health-related quality of life in patients with bladder cancer.
Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted on patients with bladder cancer in Ahvaz, 2023. Subjects were selected randomly from the patients those were registered in Cancer Registry Center in Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical sciences and invited to Golestan Hospital for data collection through clinical evaluation, the Oral Health Literacy Adult Questionnaire (OHL-AQ), and the Oral Health Impact Profile-14 (OHIP-14PER) questionnaire. The data were analyzed using Pearson correlation coefficient, independent t-test, and analysis of variance.
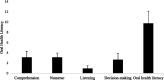
Results: The number of participants was 194. The mean oral health literacy in patients with bladder cancer was 9.74 ± 2.39, indicating insufficient oral health literacy. A significant association was observed between OHL-AQ and DMFT index, but no significant association was found between OHIP-14PER and DMFT index. Furthermore, a significant correlation was found between OHL-AQ and OHIP-14PER (r = -0.68) in patients with bladder cancer.
Conclusion: Based on the findings of the present study, all dimensions of oral health literacy have correlation with the oral health-related quality of life in patients with bladder cancer. Therefore, adopting oral health behaviors and increasing oral health literacy can be the best way to improve the oral health-related quality of life to among patients with bladder cancer.
Keywords: DMFT; Health Literacy; Oral; bladder cancer; quality of life.
Copyright © 2024 Babadi, Ahmadi, Sarkarian and Cheraghi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nowroozi MR, Amini E, Farkhani EM, Nowroozi A, Ayati M, Momeni SA, et al. . National and subnational incidence trend of bladder Cancer in Iran: report of a 12-year period. Int J Cancer Manag. (2023) 16:e127005. doi: 10.5812/ijcm-127005 - DOI
-
- Lund Håheim L, Thelle DS, Rønningen KS, Olsen I, Schwarze PE. Low level of antibodies to the oral bacterium Tannerella forsythia predicts bladder cancers and Treponema denticola predicts colon and bladder cancers: a prospective cohort study. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0272148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272148, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical