Role of erythropoietin in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: the story so far
- PMID: 38846819
- PMCID: PMC11152865
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002113
Role of erythropoietin in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: the story so far
Abstract
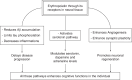
This review aims to explore the potential of erythropoietin, a glycopeptide hormone, as a treatment option for Alzheimer's disease, which is the commonest cause of dementia. Despite years of focus and research, therapeutic options for Alzheimer's disease are not yet completely satisfactory. And as people age, they are likely to develop Alzheimer's Disease, further pressuring the healthcare system. So, it is definite to develop treatment options that meet superior outcomes with minimal negative effects. A comprehensive review of the literature was conducted in PubMed and Google Scholar using a combination of keywords, including Alzheimer's disease, dementia, erythropoietin, and neuroprotection. Search results were assessed for relevance before using the data for this study. The beneficial implications of erythropoietin as a therapeutic option have been explored, along with the side effects and mechanisms of erythropoietin in Alzheimer's disease. Overall, the authors' review indicates that erythropoietin presents a promising avenue for mitigating the progression of Alzheimer's disease, with minimal associated side effects.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; dementia; erythropoietin; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroprotection.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have conflicts of interest to disclose.Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dementia of Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders--memantine, a new hope.Pharmacol Res. 2005 Jan;51(1):1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2004.05.005. Pharmacol Res. 2005. PMID: 15519530 Review.
-
Structural magnetic resonance imaging for the early diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease in people with mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 2;3(3):CD009628. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009628.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32119112 Free PMC article.
-
Postmenopausal hormone therapy and Alzheimer's disease, dementia, and Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and time-response meta-analysis.Pharmacol Res. 2020 May;155:104693. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104693. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32057896
-
Combination Therapy for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: Recent Progress and Future Prospects.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(22):1849-1867. doi: 10.2174/1568026622666220907114443. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36082857 Review.
-
Neuroprotective effects of erythropoietin on neurodegenerative and ischemic brain diseases: the role of erythropoietin receptor.Neural Regen Res. 2017 Sep;12(9):1381-1389. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.215240. Neural Regen Res. 2017. PMID: 29089974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang XX, Tian Y, Wang ZT, et al. . The epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease modifiable risk factors and prevention. J Prev Alzheimers Dis 2021;8:313–321. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease International . World Alzheimer Report 2019.Availableathttps://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2019.pdf .
-
- World Health Organization . Dementia. Accessed on September 08, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources