Body mass index, smoking behavior, and depression mediated the effects of schizophrenia on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: trans-ethnic Mendelian-randomization analysis
- PMID: 38846919
- PMCID: PMC11155452
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1405107
Body mass index, smoking behavior, and depression mediated the effects of schizophrenia on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: trans-ethnic Mendelian-randomization analysis
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have highlighted the association between schizophrenia (SCZ) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), yet the causal relationship remains unestablished.
Methods: Under the genome-wide significance threshold (P<5×10-8), data from individuals of European (EUR) and East Asian (EAS) ancestries with SCZ were selected for analysis. Univariable Mendelian randomization (MR) explored the causal relationship between SCZ and COPD. Linkage disequilibrium score (LDSC) regression was used to calculate genetic correlation, while multivariable and mediation MR further investigated the roles of six confounding factors and their mediating effects. The primary method utilized was inverse-variance weighted (IVW), complemented by a series of sensitivity analyses and false discovery rate (FDR) correction.
Results: LDSC analysis revealed a significant genetic correlation between SCZ and COPD within EUR ancestry (rg = 0.141, P = 6.16×10-7), with no such correlation found in EAS ancestry. IVW indicated a significant causal relationship between SCZ and COPD in EUR ancestry (OR = 1.042, 95% CI 1.013-1.071, P = 0.003, PFDR = 0.015). Additionally, replication datasets provide evidence of consistent causal associations(P < 0.05 & PFDR < 0.05). Multivariable and mediation MR analyses identified body mass index (BMI)(Mediation effect: 50.57%, P = 0.02), age of smoking initiation (Mediation effect: 27.42%, P = 0.02), and major depressive disorder (MDD) (Mediation effect: 60.45%, P = 6.98×10-5) as partial mediators of this causal relationship. No causal associations were observed in EAS (OR = 0.971, 95% CI 0.875-1.073, P = 0.571, PFDR = 0.761) ancestry. No causal associations were found in the reverse analysis across the four ancestries (P > 0.05 & PFDR > 0.05).
Conclusions: This study confirmed a causal relationship between SCZ and the risk of COPD in EUR ancestry, with BMI, smoking, and MDD serving as key mediators. Future research on a larger scale is necessary to validate the generalizability of these findings across other ancestries.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; causality; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; mediation analysis; schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2024 Ni, Zhang, Tang, Xiang, Cheng, Zhang and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
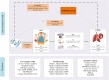



References
-
- Halpin DMG, Criner GJ, Papi A, Singh D, Anzueto A, Martinez FJ, et al. . Global initiative for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease. The 2020 GOLD science committee report on COVID-19 and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2021) 203:24–36. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202009-3533SO - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

