Contemporary Management of Pulmonary Embolism: Review of the Inferior Vena Cava filter and Other Endovascular Devices
- PMID: 38846989
- PMCID: PMC11152642
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0044-1785231
Contemporary Management of Pulmonary Embolism: Review of the Inferior Vena Cava filter and Other Endovascular Devices
Abstract
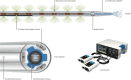
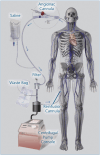
Inferior vena cava (IVC) filters and endovascular devices are used to mitigate the risk of pulmonary embolism in patients presenting with lower extremity venous thromboembolism in whom long-term anticoagulation is not a good option. However, the efficacy and benefit of these devices remain uncertain, and controversies exist. This review focuses on the current use of IVC filters and other endovascular therapies in clinical practice. The indications, risks, and benefits are discussed based on current data. Further research and randomized controlled trials are needed to characterize the patient population that would benefit most from these interventional therapies.
Keywords: IVC filter; catheter-based interventions; pulmonary embolism; thrombectomy; thrombolysis.
International College of Angiology. This article is published by Thieme.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures





References
-
- Lehnert P, Lange T, Møller C H, Olsen P S, Carlsen J. Acute pulmonary embolism in a national Danish cohort: increasing incidence and decreasing mortality. Thromb Haemost. 2018;118(03):539–546. - PubMed
-
- Galanaud J P, Laroche J P, Righini M. The history and historical treatments of deep vein thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11(03):402–411. - PubMed
-
- Kearon C, Akl E A, Ornelas J et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016;149(02):315–352. - PubMed
-
- Mobin-Uddin K, Callard G M, Bolooki H, Rubinson R, Michie D, Jude J R. Transvenous caval interruption with umbrella filter. N Engl J Med. 1972;286(02):55–58. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher A P, Alkjaersig N, Smyrniotis F E, Sherry S. The treatment of patients suffering from early myocardial infarction with massive and prolonged streptokinase therapy. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1958;71:287–296. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

