Aberrant spliceosome activity via elevated intron retention and upregulation and phosphorylation of SF3B1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 38846999
- PMCID: PMC11154714
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102202
Aberrant spliceosome activity via elevated intron retention and upregulation and phosphorylation of SF3B1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
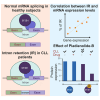
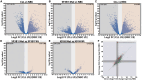
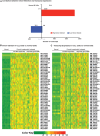
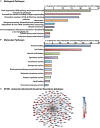
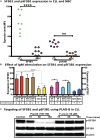
Splicing factor 3b subunit 1 (SF3B1) is the largest subunit and core component of the spliceosome. Inhibition of SF3B1 was associated with an increase in broad intron retention (IR) on most transcripts, suggesting that IR can be used as a marker of spliceosome inhibition in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells. Furthermore, we separately analyzed exonic and intronic mapped reads on annotated RNA-sequencing transcripts obtained from B cells (n = 98 CLL patients) and healthy volunteers (n = 9). We measured intron/exon ratio to use that as a surrogate for alternative RNA splicing (ARS) and found that 66% of CLL-B cell transcripts had significant IR elevation compared with normal B cells (NBCs) and that correlated with mRNA downregulation and low expression levels. Transcripts with the highest IR levels belonged to biological pathways associated with gene expression and RNA splicing. A >2-fold increase of active pSF3B1 was observed in CLL-B cells compared with NBCs. Additionally, when the CLL-B cells were treated with macrolides (pladienolide-B), a significant decrease in pSF3B1, but not total SF3B1 protein, was observed. These findings suggest that IR/ARS is increased in CLL, which is associated with SF3B1 phosphorylation and susceptibility to SF3B1 inhibitors. These data provide additional support to the relevance of ARS in carcinogenesis and evidence of pSF3B1 participation in this process.
Keywords: CLL; E7107; MT: RNA/DNA Editing; RNA splicing; RNA-seq; SF3B1; alternative RNA splicing; intron retention; intron usage; macrolide; pladienolide-B; spliceosome.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic Characterization of SF3B1 Mutation Reveals Its Pleiotropic Effects in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Cancer Cell. 2016 Nov 14;30(5):750-763. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.005. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Cancer Cell. 2016. PMID: 27818134 Free PMC article.
-
The significance of spliceosome mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2013 Jul;54(7):1364-6. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2012.742528. Epub 2013 Jan 10. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013. PMID: 23270583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SF3B1 mutation-mediated sensitization to H3B-8800 splicing inhibitor in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Aug 10;6(11):e202301955. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202301955. Print 2023 Nov. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37562845 Free PMC article.
-
The non-canonical BAF chromatin remodeling complex is a novel target of spliceosome dysregulation in SF3B1-mutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Leukemia. 2024 Nov;38(11):2429-2442. doi: 10.1038/s41375-024-02379-4. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Leukemia. 2024. PMID: 39261602 Free PMC article.
-
SF3B1 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Blood. 2013 Jun 6;121(23):4627-34. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-427641. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23568491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stilgenbauer S., Zenz T. Understanding and managing ultra high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematology. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2010;2010:481–488. - PubMed
-
- Wong J.J.L., Ritchie W., Ebner O.A., Selbach M., Wong J.W.H., Huang Y., Gao D., Pinello N., Gonzalez M., Baidya K., et al. Orchestrated intron retention regulates normal granulocyte differentiation. Cell. 2013;154:583–595. - PubMed

