Pertussis outbreak in neonates and young infants across Italy, January to May 2024: implications for vaccination strategies
- PMID: 38847118
- PMCID: PMC11158011
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2024.29.23.2400301
Pertussis outbreak in neonates and young infants across Italy, January to May 2024: implications for vaccination strategies
Abstract
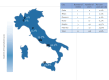
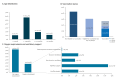
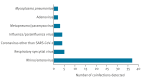
Since January 2024, Italy experiences a pertussis outbreak, primarily affecting neonates and unvaccinated infants at high risk of severe complications and mortality; 11 major paediatric centres noted 108 hospitalisations and three deaths by 10 May. The outbreak reflects increased circulation of Bordetella pertussis and non-adherence to immunisation recommendations during pregnancy. Public health interventions, including maternal immunisation, vaccination of infants as early as possible and post-exposure prophylaxis, are critical for reducing the burden of pertussis and preventing further mortality.
Keywords: Bordetella pertussis; Whooping cough; epidemic; infants; maternal immunization; newborns; outbreak; post-exposure prophylaxis; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Increase of pertussis cases in the EU/EEA. Stockholm: ECDC; 2024. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/Increase%20in%2...
