Targeted protein degradation systems to enhance Wnt signaling
- PMID: 38847394
- PMCID: PMC11161174
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.93908
Targeted protein degradation systems to enhance Wnt signaling
Abstract
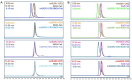
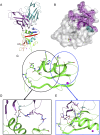
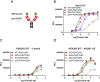
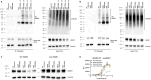
Molecules that facilitate targeted protein degradation (TPD) offer great promise as novel therapeutics. The human hepatic lectin asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGR) is selectively expressed on hepatocytes. We have previously engineered an anti-ASGR1 antibody-mutant RSPO2 (RSPO2RA) fusion protein (called SWEETS) to drive tissue-specific degradation of ZNRF3/RNF43 E3 ubiquitin ligases, which achieved hepatocyte-specific enhanced Wnt signaling, proliferation, and restored liver function in mouse models, and an antibody-RSPO2RA fusion molecule is currently in human clinical trials. In the current study, we identified two new ASGR1- and ASGR1/2-specific antibodies, 8M24 and 8G8. High-resolution crystal structures of ASGR1:8M24 and ASGR2:8G8 complexes revealed that these antibodies bind to distinct epitopes on opposing sides of ASGR, away from the substrate-binding site. Both antibodies enhanced Wnt activity when assembled as SWEETS molecules with RSPO2RA through specific effects sequestering E3 ligases. In addition, 8M24-RSPO2RA and 8G8-RSPO2RA efficiently downregulate ASGR1 through TPD mechanisms. These results demonstrate the possibility of combining different therapeutic effects and degradation mechanisms in a single molecule.
Keywords: ASGR1; LYTAC; PROTAC; R-spondin; SWEETS; Wnt; biochemistry; chemical biology; none; regenerative medicine; stem cells.
© 2024, Sampathkumar, Jung et al.
Conflict of interest statement
PS, HJ, ZZ, ZH, TL, RB, WY former full-time employee and shareholder of Surrozen, Inc, HC, NS, YY, SL, JY current full-time employee and shareholder of Surrozen, Inc, YL current full-time employee and shareholder of Surrozen, Inc; is Executive Vice President of Research at Surrozen, Inc
Figures





Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.12.08.570758
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.93908.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.93908.2
Similar articles
-
Tissue-targeted R-spondin mimetics for liver regeneration.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 18;10(1):13951. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70912-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32811902 Free PMC article.
-
Dishevelled promotes Wnt receptor degradation through recruitment of ZNRF3/RNF43 E3 ubiquitin ligases.Mol Cell. 2015 May 7;58(3):522-33. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.015. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25891077
-
ROTACs leverage signaling-incompetent R-spondin for targeted protein degradation.Cell Chem Biol. 2023 Jul 20;30(7):739-752.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.05.010. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Cell Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37321224
-
Control of Wnt Receptor Turnover by R-spondin-ZNRF3/RNF43 Signaling Module and Its Dysregulation in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2016 Jun 8;8(6):54. doi: 10.3390/cancers8060054. Cancers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27338477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The R-spondin/Lgr5/Rnf43 module: regulator of Wnt signal strength.Genes Dev. 2014 Feb 15;28(4):305-16. doi: 10.1101/gad.235473.113. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24532711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted degradation of extracellular proteins: state of the art and diversity of degrader designs.J Hematol Oncol. 2025 May 1;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13045-025-01703-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40307925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induced proximity at the cell surface.Nat Biotechnol. 2025 May;43(5):702-711. doi: 10.1038/s41587-025-02592-1. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Nat Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40140559 Review.
-
Hepatic Dyrk1b impairs systemic glucose homeostasis by modulating Wbp2 expression in a kinase activity-dependent manner.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 22;10(17):e36726. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36726. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39296215 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

