Proactive consultation of laboratory medicine increased diagnostic rate of multiple myeloma: One single center's 12-year experience
- PMID: 38847713
- PMCID: PMC11155562
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038523
Proactive consultation of laboratory medicine increased diagnostic rate of multiple myeloma: One single center's 12-year experience
Abstract
Multiple myeloma (MM) was one of the hardest cancers to diagnose because of numerous nonspecific symptoms, leading to diagnostic delay. Proactive consultation of laboratory medicine (PCLM) could help timely diagnosis of blood cancers, avoiding diagnostic delay. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of PCLM on diagnosis and outcomes in MM. This retrospective study was conducted in newly diagnosed MM patients from 2011 to 2022. Implementation of PCLM initiated in 2015 with a laboratory-oriented algorithm. The annual diagnostic rate, patient demographics, the time intervals from symptom onset to diagnosis and to treatment, and clinical outcomes were analyzed. A total of 134 patients were newly diagnosed during the study interval. The diagnostic rate increased from 4.65 ± 1.59 to 7.43 ± 1.52 per million patient-visits after implementation of PCLM. The median time interval from symptom onset to diagnosis was significantly shortened after implementation of PCLM (50 days with interquartile range [IQR]: 24-136 days vs 150 days with IQR: 41-385 days, P = .003). Besides, the 1-year survival was significantly higher in patients diagnosed as MM after implementation of PCLM (72.4% vs 51.7%, P = .035). Implementation of PCLM not only increased diagnostic rate of MM and improved outcomes, but also raise awareness for MM and promote multidisciplinary collaboration in healthcare.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
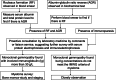
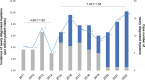
References
-
- Myeloma Incidence Statistics. Cancer Research UK. https:/www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/st.... Accessed March 8, 2024.
-
- Incidence and mortality rates for the top 10 cancer in Taiwan. Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare; 2020. https://twcr.tw/?page_id=1855&lang=en. Accessed March 8, 2024.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

