The predictive value of delta-like3 and serum NSE in evaluating chemotherapy response and prognosis in patients with advanced small cell lung carcinoma: An observational study
- PMID: 38847733
- PMCID: PMC11155540
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038487
The predictive value of delta-like3 and serum NSE in evaluating chemotherapy response and prognosis in patients with advanced small cell lung carcinoma: An observational study
Abstract
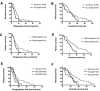
Lung cancer is one of the most malignant tumors with fastest morbidity and mortality. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is the most malignant pathological type of lung cancer with early metastasis and poor prognosis. At present, there is a lack of effective indicators to predict prognosis of SCLC patients. Delta-like 3 protein (DLL3) is selectively expressed on the surface of SCLC and is involved in proliferation and invasion. Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) is an enolase isoenzyme that is generally regarded as a biomarker for SCLC and may correlate with stage of SCLC, prognosis and chemotherapy response. NSE can be influenced by different types of factors. To explore the associations between expression levels of DLL3 in tumor tissues with platinum/etoposide chemotherapy response, and assess the prognostic values of DLL3, NSE and other potential prognostic factors in advanced SCLC patients were herein studied. Ninety-seven patients diagnosed with SCLC in Zhongda Hospital from 2014 to 2020 were enrolled in the study. Serum NSE levels were tested using ELISA methods before any treatment. The expression of DLL3 in tumor tissue was detected by Immunohistochemistry (IHC). We investigated the relationship of DLL3 expression with chemotherapy and survival. Progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method. Multivariate Cox-proportional hazard regression was used to identify predictors of PFS and OS. DLL3 was detected in 84.5% (82/97) of all patients' tumor samples by IHC, mainly located on the surface of SCLC cells. Lower DLL3 expression was associated with longer PFS and better chemotherapy response. OS had no significant differences. Multivariate analysis by Cox Hazard model showed that, high DLL3 expression and maximum tumor size >5 cm were independent risk factors for PFS, where NSE < 35 ng/mL and age < 70 were independent prognostic factors for OS. Early stage was independent prognostic factors for PFS and OS (P < .05 log-rank). DLL3 was expressed in the most of SCLCs. DLL3 expression level in the tumor and NSE level in the serum may be useful biomarkers to predict the prognosis of SCLC. DLL3 may be a potential therapeutic target for SCLC in the future.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Lo RG, Macerelli M, Platania M, et al. Small-cell lung cancer: clinical management and unmet needs new perspectives for an old problem. Curr Drug Targets. 2017;18:341–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

