Lineage specification in glioblastoma is regulated by METTL7B
- PMID: 38848215
- PMCID: PMC11220825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114309
Lineage specification in glioblastoma is regulated by METTL7B
Abstract
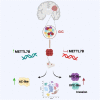
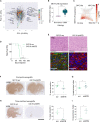
Glioblastomas are the most common malignant brain tumors in adults; they are highly aggressive and heterogeneous and show a high degree of plasticity. Here, we show that methyltransferase-like 7B (METTL7B) is an essential regulator of lineage specification in glioblastoma, with an impact on both tumor size and invasiveness. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of these tumors and of cerebral organoids derived from expanded potential stem cells overexpressing METTL7B reveal a regulatory role for the gene in the neural stem cell-to-astrocyte differentiation trajectory. Mechanistically, METTL7B downregulates the expression of key neuronal differentiation players, including SALL2, via post-translational modifications of histone marks.
Keywords: CP: Cancer; CP: Stem cell research; METTL7B; SALL2; cancer stem cells; cerebral organoids; epigenetics; glioblastoma; in vivo models; lineage specification; neural stem cells; single-cell transcriptomic.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Novel Peripherally Derived Neural-Like Stem Cells as Therapeutic Carriers for Treating Glioblastomas.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Feb;6(2):471-481. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2016-0007. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28191774 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell characteristics in glioblastoma are maintained by the ecto-nucleotidase E-NPP1.Cell Death Differ. 2014 Jun;21(6):929-40. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.12. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Cell Death Differ. 2014. PMID: 24531536 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive Notch2 signaling in neural stem cells promotes tumorigenic features and astroglial lineage entry.Cell Death Dis. 2012 Jun 21;3(6):e325. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.65. Cell Death Dis. 2012. PMID: 22717580 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of tumor-suppressive microRNA-218 in targeting glioblastoma stemness.Cancer Lett. 2014 Oct 10;353(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.07.011. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25042866 Review.
-
An update on the epigenetics of glioblastomas.Epigenomics. 2016 Sep;8(9):1289-305. doi: 10.2217/epi-2016-0040. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Epigenomics. 2016. PMID: 27585647 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel model of glioblastoma recurrence to identify therapeutic vulnerabilities.EMBO Mol Med. 2025 Jun;17(6):1325-1354. doi: 10.1038/s44321-025-00237-z. Epub 2025 Apr 28. EMBO Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40295888 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Glioblastoma Research with Innovative Brain Organoid-Based Models.Cells. 2025 Feb 16;14(4):292. doi: 10.3390/cells14040292. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39996764 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Raviram R., Raman A., Preissl S., Ning J., Wu S., Koga T., Zhang K., Brennan C.W., Zhu C., Luebeck J., et al. Integrated analysis of single-cell chromatin state and transcriptome identified common vulnerability despite glioblastoma heterogeneity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2023;120 doi: 10.1073/pnas.2210991120. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

