Understanding the biosynthesis of human IgM SAM-6 through a combinatorial expression of mutant subunits that affect product assembly and secretion
- PMID: 38848420
- PMCID: PMC11161108
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291568
Understanding the biosynthesis of human IgM SAM-6 through a combinatorial expression of mutant subunits that affect product assembly and secretion
Abstract
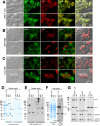
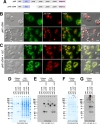
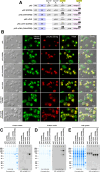
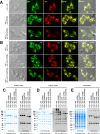
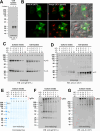
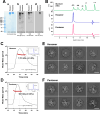
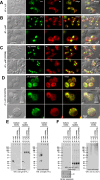
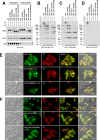
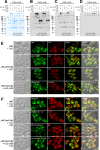
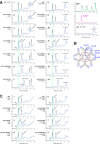
Polymeric IgMs are secreted from plasma cells abundantly despite their structural complexity and intricate multimerization steps. To gain insights into IgM's assembly mechanics that underwrite such high-level secretion, we characterized the biosynthetic process of a natural human IgM, SAM-6, using a heterologous HEK293(6E) cell platform that allowed the production of IgMs both in hexameric and pentameric forms in a controlled fashion. By creating a series of mutant subunits that differentially disrupt secretion, folding, and specific inter-chain disulfide bond formation, we assessed their effects on various aspects of IgM biosynthesis in 57 different subunit chain combinations, both in hexameric and pentameric formats. The mutations caused a spectrum of changes in steady-state subcellular subunit distribution, ER-associated inclusion body formation, intracellular subunit detergent solubility, covalent assembly, secreted IgM product quality, and secretion output. Some mutations produced differential effects on product quality depending on whether the mutation was introduced to hexameric IgM or pentameric IgM. Through this systematic combinatorial approach, we consolidate diverse overlapping knowledge on IgM biosynthesis for both hexamers and pentamers, while unexpectedly revealing that the loss of certain inter-chain disulfide bonds, including the one between μHC and λLC, is tolerated in polymeric IgM assembly and secretion. The findings highlight the differential roles of underlying non-covalent protein-protein interactions in hexamers and pentamers when orchestrating the initial subunit interactions and maintaining the polymeric IgM product integrity during ER quality control steps, secretory pathway trafficking, and secretion.
Copyright: © 2024 Hasegawa et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How J-chain ensures the assembly of immunoglobulin IgM pentamers.EMBO J. 2025 Jan;44(2):505-533. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00317-9. Epub 2024 Dec 4. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 39632981 Free PMC article.
-
Late events in assembly determine the polymeric structure and biological activity of secretory IgM.Mol Immunol. 1997 Mar;34(4):323-31. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(97)00029-1. Mol Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9244345
-
J chain synthesis and secretion of hexameric IgM is differentially regulated by lipopolysaccharide and interleukin 5.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):962-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.962. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. PMID: 1736312 Free PMC article.
-
Missing links in antibody assembly control.Int J Cell Biol. 2013;2013:606703. doi: 10.1155/2013/606703. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Int J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24489546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Polymeric Immunoglobulin Receptor in IgA and IgM Transcytosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 25;22(5):2284. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052284. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33668983 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

