Mechanistic computational modeling of monospecific and bispecific antibodies targeting interleukin-6/8 receptors
- PMID: 38848446
- PMCID: PMC11189202
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012157
Mechanistic computational modeling of monospecific and bispecific antibodies targeting interleukin-6/8 receptors
Abstract
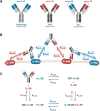
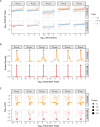
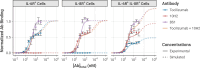
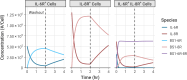
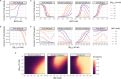
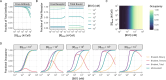
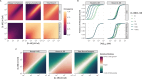
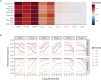
The spread of cancer from organ to organ (metastasis) is responsible for the vast majority of cancer deaths; however, most current anti-cancer drugs are designed to arrest or reverse tumor growth without directly addressing disease spread. It was recently discovered that tumor cell-secreted interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) synergize to enhance cancer metastasis in a cell-density dependent manner, and blockade of the IL-6 and IL-8 receptors (IL-6R and IL-8R) with a novel bispecific antibody, BS1, significantly reduced metastatic burden in multiple preclinical mouse models of cancer. Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs), which combine two different antigen-binding sites into one molecule, are a promising modality for drug development due to their enhanced avidity and dual targeting effects. However, while BsAbs have tremendous therapeutic potential, elucidating the mechanisms underlying their binding and inhibition will be critical for maximizing the efficacy of new BsAb treatments. Here, we describe a quantitative, computational model of the BS1 BsAb, exhibiting how modeling multivalent binding provides key insights into antibody affinity and avidity effects and can guide therapeutic design. We present detailed simulations of the monovalent and bivalent binding interactions between different antibody constructs and the IL-6 and IL-8 receptors to establish how antibody properties and system conditions impact the formation of binary (antibody-receptor) and ternary (receptor-antibody-receptor) complexes. Model results demonstrate how the balance of these complex types drives receptor inhibition, providing important and generalizable predictions for effective therapeutic design.
Copyright: © 2024 Ray et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: Johns Hopkins University has filed intellectual property on technologies described herein with HY and JBS listed as inventors (WO2020243479A1 and WO2020243489A1).
Figures
Update of
-
Mechanistic computational modeling of monospecific and bispecific antibodies targeting interleukin-6/8 receptors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 19:2023.12.18.570445. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.18.570445. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Jun 7;20(6):e1012157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012157. PMID: 38187701 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Petersen F, Flad HD, Brandt E. Neutrophil-activating peptides NAP-2 and IL-8 bind to the same sites on neutrophils but interact in different ways. Discrepancies in binding affinities, receptor densities, and biologic effects. J Immunol 1994;152(5):2467–2478. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.152.5.2467 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

