Shared Genetic Architecture Between Schizophrenia and Anorexia Nervosa: A Cross-trait Genome-Wide Analysis
- PMID: 38848516
- PMCID: PMC11349005
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbae087
Shared Genetic Architecture Between Schizophrenia and Anorexia Nervosa: A Cross-trait Genome-Wide Analysis
Abstract
Background and hypothesis: Schizophrenia (SCZ) and anorexia nervosa (AN) are 2 severe and highly heterogeneous disorders showing substantial familial co-aggregation. Genetic factors play a significant role in both disorders, but the shared genetic etiology between them is yet to be investigated.
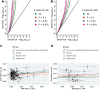
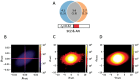
Study design: Using summary statistics from recent large genome-wide association studies on SCZ (Ncases = 53 386) and AN (Ncases = 16 992), a 2-sample Mendelian randomization analysis was conducted to explore the causal relationship between SCZ and AN. MiXeR was employed to quantify their polygenic overlap. A conditional/conjunctional false discovery rate (condFDR/conjFDR) framework was adopted to identify loci jointly associated with both disorders. Functional annotation and enrichment analyses were performed on the shared loci.
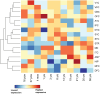
Study results: We observed a cross-trait genetic enrichment, a suggestive bidirectional causal relationship, and a considerable polygenic overlap (Dice coefficient = 62.2%) between SCZ and AN. The proportion of variants with concordant effect directions among all shared variants was 69.9%. Leveraging overlapping genetic associations, we identified 6 novel loci for AN and 33 novel loci for SCZ at condFDR <0.01. At conjFDR <0.05, we identified 10 loci jointly associated with both disorders, implicating multiple genes highly expressed in the cerebellum and pituitary and involved in synapse organization. Particularly, high expression of the shared genes was observed in the hippocampus in adolescence and orbitofrontal cortex during infancy.
Conclusions: This study provides novel insights into the relationship between SCZ and AN by revealing a shared genetic component and offers a window into their complex etiology.
Keywords: GWAS; Mendelian randomization; anorexia; architecture; genetic; nervosa; pleiotropy; polygenic overlap; schizophrenia.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center.
Figures

References
-
- Jauhar S, Johnstone M, McKenna PJ.. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2022;399(10323):473–486. - PubMed
-
- Arcelus J, Mitchell AJ, Wales J, Nielsen S.. Mortality rates in patients with anorexia nervosa and other eating disorders. A meta-analysis of 36 studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68(7):724–731. - PubMed
-
- Treasure J, Duarte TA, Schmidt U.. Eating disorders. Lancet. 2020;395(10227):899–911. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

