Is the peripheral microcirculation a window into the human coronary microvasculature?
- PMID: 38848808
- PMCID: PMC11260236
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2024.06.002
Is the peripheral microcirculation a window into the human coronary microvasculature?
Abstract
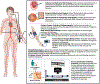
An increasing body of evidence suggests a pivotal role for the microvasculature in the development of cardiovascular disease. A dysfunctional coronary microvascular network, specifically within endothelial cells-the inner most cell layer of vessels-is considered a strong, independent risk factor for future major adverse cardiac events. However, challenges exist with evaluating this critical vascular bed, as many of the currently available techniques are highly invasive and cost prohibitive. The more easily accessible peripheral microcirculation has surfaced as a potential surrogate in which to study mechanisms of coronary microvascular dysfunction and likewise may be used to predict poor cardiovascular outcomes. In this review, we critically evaluate a variety of prognostic, physiological, and mechanistic studies in humans to answer whether the peripheral microcirculation can add insight into coronary microvascular health. A conceptual framework is proposed that the health of the endothelium specifically may link the coronary and peripheral microvascular beds. This is supported by evidence showing a correlation between human coronary and peripheral endothelial function in vivo. Although not a replacement for investigating and understanding coronary microvascular function, the microvascular endothelium from the periphery responds similarly to (patho)physiological stress and may be leveraged to explore potential therapeutic pathways to mitigate stress-induced damage.
Keywords: Coronary; Endothelium; Microvasculature; Translational.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Camilleri JP, Fabiani JN. No-reflow phenomenon and acute myocardial ischemia. The need for further investigation. Biomedicine. 1977;26(6):353–6. - PubMed
-
- van de Hoef TP, Bax M, Damman P, Delewi R, Hassell ME, Piek MA, et al. Impaired Coronary Autoregulation Is Associated With Long-term Fatal Events in Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6(4):329–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

