Structural basis for inhibition of coagulation factor VIII reveals a shared antigenic hotspot on the C1 domain
- PMID: 38849084
- PMCID: PMC11343672
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtha.2024.05.024
Structural basis for inhibition of coagulation factor VIII reveals a shared antigenic hotspot on the C1 domain
Abstract
Background: Hemophilia A arises from dysfunctional or deficient coagulation factor (F)VIII and leads to inefficient fibrin clot formation and uncontrolled bleeding events. The development of antibody inhibitors is a clinical complication in hemophilia A patients receiving FVIII replacement therapy. LE2E9 is an anti-C1 domain inhibitor previously isolated from a mild/moderate hemophilia A patient and disrupts FVIII interactions with von Willebrand factor and FIXa, though the intermolecular contacts that underpin LE2E9-mediated FVIII neutralization are undefined.
Objectives: To determine the structure of the complex between FVIII and LE2E9 and characterize its mechanism of inhibition.
Methods: FVIII was bound to the antigen binding fragment (Fab) of NB2E9, a recombinant construct of LE2E9, and its structure was determined by cryogenic electron microscopy.
Results: This report communicates the 3.46 Å structure of FVIII bound to NB2E9, with its epitope comprising FVIII residues S2040 to Y2043, K2065 to W2070, and R2150 to H2155. Structural analysis reveals that the LE2E9 epitope overlaps with portions of the epitope for 2A9, a murine-derived inhibitor, suggesting that these residues represent a shared antigenic region on the C1 domain between FVIII-/- mice and hemophilia A patients. Furthermore, the FVIII:NB2E9 structure elucidates the orientation of the LE2E9 glycan, illustrating how the glycan sterically blocks interactions between the FVIII C1 domain and the von Willebrand factor D' domain. A putative model of the FVIIIa:FIXa complex suggests potential clashing between the NB2E9 glycan and FIXa light chain.
Conclusion: These results describe an antigenic "hotspot" on the FVIII C1 domain and provide a structural basis for engineering FVIII replacement therapeutics with reduced antigenicity.
Keywords: antibody inhibitor; blood coagulation; cryoelectron microscopy; factor VIII; hemophilia.
Copyright © 2024 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interests P.L. is listed as an inventor on a patent application describing ET3i and on patents owned by Emory University claiming compositions of matter that include modified FVIII proteins with reduced reactivity with anti-FVIII antibodies. C.B.D. and P.L. are cofounders of Expression Therapeutics and own equity in the company. Expression Therapeutics owns the intellectual property associated with ET3i. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by Emory University in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies. The remaining authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures




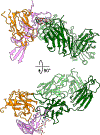

References
-
- Fay PJ. Factor VIII structure and function. Int J Hematol 2006; 83: 103–8. - PubMed
-
- Leyte A, Van Schijndel HB, Niehrs C, Huttner WB, Verbeet MP, Mertens K, Van Mourik JA. Sulfation of Tyr1680 of human blood coagulation Factor VIII is essential for the interaction of Factor VIII with von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 740–6. - PubMed
-
- Wise RJ, Dorner AJ, Krane M, Pittman DD, Kaufman RJ. The role of von Willebrand factor multimers and propeptide cleavage in binding and stabilization of factor VIII. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 21948–55. - PubMed
-
- Lollar P. Pathogenic antibodies to coagulation factors. Part one: Factor VIII and Factor IX. J Thromb Haemost 2004; 2: 1082–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

