Systemic inflammation, oxidative damage and neurocognition predict telomere length in a transdiagnostic sample stratified by global DNA methylation levels
- PMID: 38849401
- PMCID: PMC11161596
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-62980-6
Systemic inflammation, oxidative damage and neurocognition predict telomere length in a transdiagnostic sample stratified by global DNA methylation levels
Abstract
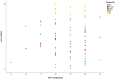
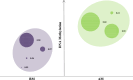
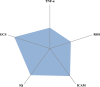
Epigenetic mechanisms contribute to the maintenance of both type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and psychiatric disorders. Emerging evidence suggests that molecular pathways and neurocognitive performance regulate epigenetic dynamics in these disorders. The current combined and transdiagnostic study investigated whether inflammatory, oxidative stress, adhesion molecule, neurocognitive and functional performance are significant predictors of telomere dynamics in a sample stratified by global DNA methylation levels. Peripheral blood inflammation, oxidative stress and adhesion molecule biomarkers and neurocognitive function were assessed twice over a 1-year period in 80 individuals, including 16 with schizophrenia (SZ), 16 with bipolar disorder (BD), 16 with major depressive disorder (MDD), 15 with T2DM, and 17 healthy controls (HCs). Leukocyte telomere length (LTL) was measured by qRT-PCR using deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extracted from peripheral blood samples. A posteriori, individuals were classified based on their global methylation score (GMS) at baseline into two groups: the below-average methylation (BM) and above-average methylation (AM) groups. Hierarchical and k-means clustering methods, mixed one-way analysis of variance and linear regression analyses were performed. Overall, the BM group showed a significantly higher leukocyte telomere length (LTL) than the AM group at both time points (p = 0.02; η2p = 0.06). Moreover, the BM group had significantly lower levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) (p = 0.03; η2p = 0.06) and C-reactive protein (CRP) (p = 0.03; η2p = 0.06) than the AM group at the 1-year follow-up. Across all participants, the regression models showed that oxidative stress (reactive oxygen species [ROS]) (p = 0.04) and global cognitive score [GCS] (p = 0.02) were significantly negatively associated with LTL, whereas inflammatory (TNF-α) (p = 0.04), adhesion molecule biomarkers (inter cellular adhesion molecule [ICAM]) (p = 0.009), and intelligence quotient [IQ] (p = 0.03) were significantly positively associated with LTL. Moreover, the model predictive power was increased when tested in both groups separately, explaining 15.8% and 28.1% of the LTL variance at the 1-year follow-up for the AM and BM groups, respectively. Heterogeneous DNA methylation in individuals with T2DM and severe mental disorders seems to support the hypothesis that epigenetic dysregulation occurs in a transdiagnostic manner. Our results may help to elucidate the interplay between epigenetics, molecular processes and neurocognitive function in these disorders. DNA methylation and LTL are potential therapeutic targets for transdiagnostic interventions to decrease the risk of comorbidities.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
VB-M has been a Continuing Medical Education (CME) speaker over the last 3 years for Angelini, unrelated to the present work. All other authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

