An enhanced speech emotion recognition using vision transformer
- PMID: 38849422
- PMCID: PMC11161461
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-63776-4
An enhanced speech emotion recognition using vision transformer
Abstract
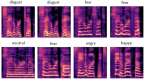
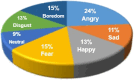
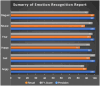
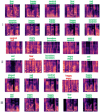
In human-computer interaction systems, speech emotion recognition (SER) plays a crucial role because it enables computers to understand and react to users' emotions. In the past, SER has significantly emphasised acoustic properties extracted from speech signals. The use of visual signals for enhancing SER performance, however, has been made possible by recent developments in deep learning and computer vision. This work utilizes a lightweight Vision Transformer (ViT) model to propose a novel method for improving speech emotion recognition. We leverage the ViT model's capabilities to capture spatial dependencies and high-level features in images which are adequate indicators of emotional states from mel spectrogram input fed into the model. To determine the efficiency of our proposed approach, we conduct a comprehensive experiment on two benchmark speech emotion datasets, the Toronto English Speech Set (TESS) and the Berlin Emotional Database (EMODB). The results of our extensive experiment demonstrate a considerable improvement in speech emotion recognition accuracy attesting to its generalizability as it achieved 98%, 91%, and 93% (TESS-EMODB) accuracy respectively on the datasets. The outcomes of the comparative experiment show that the non-overlapping patch-based feature extraction method substantially improves the discipline of speech emotion recognition. Our research indicates the potential for integrating vision transformer models into SER systems, opening up fresh opportunities for real-world applications requiring accurate emotion recognition from speech compared with other state-of-the-art techniques.
Keywords: CNN; Deep learning; Human–computer interaction; Mel spectrogram; Speech emotion recognition; Vision transformer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MelTrans: Mel-Spectrogram Relationship-Learning for Speech Emotion Recognition via Transformers.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Aug 25;24(17):5506. doi: 10.3390/s24175506. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39275417 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-dilated convolution network for speech emotion recognition.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 10;15(1):8254. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92640-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40064942 Free PMC article.
-
Fusing Visual Attention CNN and Bag of Visual Words for Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Sep 28;20(19):5559. doi: 10.3390/s20195559. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32998382 Free PMC article.
-
Random Deep Belief Networks for Recognizing Emotions from Speech Signals.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2017;2017:1945630. doi: 10.1155/2017/1945630. Epub 2017 Mar 5. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28356908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Learning Techniques for Speech Emotion Recognition, from Databases to Models.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 10;21(4):1249. doi: 10.3390/s21041249. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33578714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual prompt personalized federated learning in foundation models.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 31;15(1):28026. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11864-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40745444 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-modal gated feature enhancement for multimodal emotion recognition in conversations.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 16;15(1):30004. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11989-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40819129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yahia, A. C., Moussaoui, Frahta, N. & Moussaoui, A. Effective speech emotion recognition using deep learning approaches for Algerian Dialect. In In Proc. Intl. Conf. of Women in Data Science at Taif University, WiDSTaif 1–6 (2021). 10.1109/WIDSTAIF52235.2021.9430224
-
- Blackwell, A. Human Computer Interaction-Lecture Notes Cambridge Computer Science Tripos, Part II. https://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/teaching/1011/HCI/HCI2010.pdf (2010)
-
- Muthusamy, K. H., Polat, Yaacob, S. Improved emotion recognition using gaussian mixture model and extreme learning machine in speech and glottal signals. Math. Probl. Eng. (2015). 10.1155/2015/394083
-
- Xie J, Zhu M, Hu K. Fusion-based speech emotion classification using two-stage feature selection. Speech Commun. 2023;66(6):102955. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2023.102955. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

