Systematic assessment of long-read RNA-seq methods for transcript identification and quantification
- PMID: 38849569
- PMCID: PMC11543605
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-024-02298-3
Systematic assessment of long-read RNA-seq methods for transcript identification and quantification
Abstract
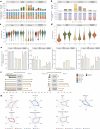
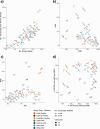
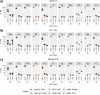
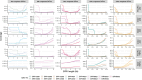
The Long-read RNA-Seq Genome Annotation Assessment Project Consortium was formed to evaluate the effectiveness of long-read approaches for transcriptome analysis. Using different protocols and sequencing platforms, the consortium generated over 427 million long-read sequences from complementary DNA and direct RNA datasets, encompassing human, mouse and manatee species. Developers utilized these data to address challenges in transcript isoform detection, quantification and de novo transcript detection. The study revealed that libraries with longer, more accurate sequences produce more accurate transcripts than those with increased read depth, whereas greater read depth improved quantification accuracy. In well-annotated genomes, tools based on reference sequences demonstrated the best performance. Incorporating additional orthogonal data and replicate samples is advised when aiming to detect rare and novel transcripts or using reference-free approaches. This collaborative study offers a benchmark for current practices and provides direction for future method development in transcriptome analysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The design of the project was discussed with ONT, PacBio and Lexogen. ONT provided partial support for flow cells and reagents. H.U.T. and A. Conesa have, in the past, presented at events organized by PacBio and have received reimbursement or support for travel, accommodation and conference fees. H.U.T. has also spoken at local ONT events during the duration of this project and received food. Unrelated to this project, the laboratory of H.U.T. has purchased reagents from Illumina, PacBio and ONT at discounted prices. S.C.-S., A.N.B. and J.G. have received reimbursement for travel, accommodation and conference fees to speak at events organized by ONT. A.N.B. is a consultant for Remix Therapeutics. A. Conesa is the founder of Biobam Bioinformatics. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Update of
-
Systematic assessment of long-read RNA-seq methods for transcript identification and quantification.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 27:2023.07.25.550582. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.25.550582. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Methods. 2024 Jul;21(7):1349-1363. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02298-3. PMID: 37546854 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HG008759/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES030283/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HG011280/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM133569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM138122/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG007182/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U41HG007234/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- UM1 HG009443/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 73023672/Saint Petersburg State University (St. Petersburg State University)
- WT108749/Z/15/Z/Wellcome Trust (Wellcome)
- R35 GM142647/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35GM138122/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- UM1 HG009402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- F31HG010999/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- U41 HG007234/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG011469/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HG010999/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG008759/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- R01HG011469/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- R01GM136886/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- R35GM14264/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

