Dapagliflozin reduces systemic inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes without known heart failure
- PMID: 38849829
- PMCID: PMC11161924
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02294-z
Dapagliflozin reduces systemic inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes without known heart failure
Abstract
Objective: Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors significantly improve cardiovascular outcomes in diabetic patients; however, the mechanism is unclear. We hypothesized that dapagliflozin improves cardiac outcomes via beneficial effects on systemic and cardiac inflammation and cardiac fibrosis.
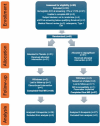
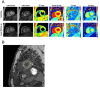
Research and design methods: This randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial enrolled 62 adult patients (mean age 62, 17% female) with type 2 diabetes (T2D) without known heart failure. Subjects were randomized to 12 months of daily 10 mg dapagliflozin or placebo. For all patients, blood/plasma samples and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMRI) were obtained at time of randomization and at the end of 12 months. Systemic inflammation was assessed by plasma IL-1B, TNFα, IL-6 and ketone levels and PBMC mitochondrial respiration, an emerging marker of sterile inflammation. Global myocardial strain was assessed by feature tracking; cardiac fibrosis was assessed by T1 mapping to calculate extracellular volume fraction (ECV); and cardiac tissue inflammation was assessed by T2 mapping.
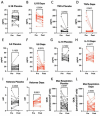
Results: Between the baseline and 12-month time point, plasma IL-1B was reduced (- 1.8 pg/mL, P = 0.003) while ketones were increased (0.26 mM, P = 0.0001) in patients randomized to dapagliflozin. PBMC maximal oxygen consumption rate (OCR) decreased over the 12-month period in the placebo group but did not change in patients receiving dapagliflozin (- 158.9 pmole/min/106 cells, P = 0.0497 vs. - 5.2 pmole/min/106 cells, P = 0.41), a finding consistent with an anti-inflammatory effect of SGLT2i. Global myocardial strain, ECV and T2 relaxation time did not change in both study groups.
Gov registration: NCT03782259.
Keywords: CMRI; Cardiac fibrosis; IL-1B; Inflammation; PBMC respiration; SGLT2 inhibitor; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
Dapagliflozin Reduces Systemic Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Without Known Heart Failure.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 25:rs.3.rs-4132581. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4132581/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Jun 7;23(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02294-z. PMID: 38585865 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 with and without type 2 diabetes: a prespecified analysis of the DARE-19 randomized trial.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jul 30;24(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02875-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40739638 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dapagliflozin Reduces Systemic Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Without Known Heart Failure.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 25:rs.3.rs-4132581. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4132581/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Jun 7;23(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02294-z. PMID: 38585865 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Impact of SGLT2 inhibitors on myocardial fibrosis in diabetic HFpEF: a longitudinal study.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 8;30(1):592. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02834-7. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40624547 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sodium-glucose co-transporter protein 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for people with chronic kidney disease and diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 21;5(5):CD015588. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015588.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38770818 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on cardiovascular events, death, and major safety outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016 May;4(5):411-9. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(16)00052-8. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27009625
Cited by
-
Critical Appraisal of Pharmaceutical Therapy in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy-Challenges and Prospectives.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 20;18(1):134. doi: 10.3390/ph18010134. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into FGF21 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy by suppressing ferroptosis: a commentary.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Nov 26;23(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02519-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39593068 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dapagliflozin on the serum metabolome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024 Dec 16;24(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s40200-024-01508-1. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024. PMID: 39697865
-
Dapagliflozin ameliorates Lafora disease phenotype in a zebrafish model.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 Feb;183:117800. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117800. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 39753095 Free PMC article.
-
Shedding light on the effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in the early stages of heart failure.World J Cardiol. 2025 Mar 26;17(3):102893. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i3.102893. World J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40161565 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

