Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Helicobacter pylori Infection Study in Adults
- PMID: 38850016
- PMCID: PMC11168235
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943666
Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Helicobacter pylori Infection Study in Adults
Abstract
BACKGROUND Helicobacter pylori has a high infection rate worldwide, and epidemiological study of H. pylori is important. Artificial intelligence has been widely used in the field of medical research and has become a hotspot in recent years. This paper proposed a prediction model for H. pylori infection based on machine learning in adults. MATERIAL AND METHODS Adult patients were selected as research participants, and information on 30 factors was collected. The chi-square test, mutual information, ReliefF, and information gain were used to screen the feature factors and establish 2 subsets. We constructed an H. pylori infection prediction model based on XGBoost and optimized the model using a grid search by analyzing the correlation between features. The performance of the model was assessed by comparing its accuracy, recall, precision, F1 score, and AUC with those of 4 other classical machine learning methods. RESULTS The model performed better on the part B subset than on the part A subset. Compared with the other 4 machine learning methods, the model had the highest accuracy, recall, F1 score, and AUC. SHAP was used to evaluate the importance of features in the model. It was found that H. pylori infection of family members, living in rural areas, poor washing hands before meals and after using the toilet were risk factors for H. pylori infection. CONCLUSIONS The model proposed in this paper is superior to other models in predicting H. pylori infection and can provide a scientific basis for identifying the population susceptible to H. pylori and preventing H. pylori infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
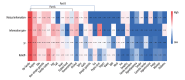
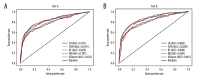
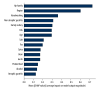

Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) risk factor analysis and prevalence prediction: a machine learning-based approach.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Jul 28;22(1):655. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07625-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35902812 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of machine learning models in the prediction of gastric cancer risk in patients after Helicobacter pylori eradication.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Apr;53(8):864-872. doi: 10.1111/apt.16272. Epub 2021 Jan 24. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33486805
-
Artificial Intelligence for the Prediction of Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Endoscopic Images: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Of Diagnostic Test Accuracy.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Sep 16;22(9):e21983. doi: 10.2196/21983. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32936088 Free PMC article.
-
A survey on Helicobacter pylori infection rate in Hainan Province and analysis of related risk factors.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Sep 30;23(1):338. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02973-3. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37777740 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori: epidemiology and routes of transmission.Epidemiol Rev. 2000;22(2):283-97. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a018040. Epidemiol Rev. 2000. PMID: 11218379 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning for prediction of Helicobacter pylori infection based on basic health examination data in adults: a retrospective study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 13;12:1587540. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1587540. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40584706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hooi J, Lai WY, Ng WK, et al. Global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(2):420–29. - PubMed
-
- Ren S, Cai P, Liu Y, et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;37(3):464–70. - PubMed
-
- Yuan G, Chen Y, He S. Family history of gastric cancer and Helicobacter pylori treatment. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(22):2171. - PubMed
-
- Al-Khalidy HSH. Obesity and Helicobacter pylori infection in adults with non specific colitis. J Coloproctol. 2020;40(2):168–71.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

