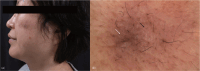
An Asymptomatic Brown Plaque on the Face: A Quiz
- PMID: 38850053
- PMCID: PMC11181913
- DOI: 10.2340/actadv.v104.40377
An Asymptomatic Brown Plaque on the Face: A Quiz
Figures
Similar articles
-
Yellow-brown Papules on the Cheeks and Limbs of a Male Infant: A Quiz.Acta Derm Venereol. 2018 Jun 8;98(6):620-621. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2907. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018. PMID: 29437191 No abstract available.
-
Dyskeratosis of the Face: A Quiz.Acta Derm Venereol. 2016 Feb;96(2):285-7. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2207. Acta Derm Venereol. 2016. PMID: 26258665 No abstract available.
-
A Woman with Red Edematous Erythema of the Face: A Quiz.Acta Derm Venereol. 2024 Aug 7;104:adv40766. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v104.40766. Acta Derm Venereol. 2024. PMID: 39113340 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
[Facial manifestations of granulomatous diseases].Hautarzt. 2017 Jul;68(7):542-547. doi: 10.1007/s00105-017-3994-4. Hautarzt. 2017. PMID: 28593339 Review. German.
-
Unilateral facial actinic elastotic plaque--a new clinical variant of actinic elastosis.Australas J Dermatol. 1989;30(1):15-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.1989.tb00401.x. Australas J Dermatol. 1989. PMID: 2486047 Review.
References
-
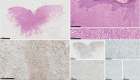
- Gomez-Moyano E, Vera-Casano A, Martinez-Garcia S, Sanz-Trelles A, Crespo-Erchiga V. Two cases of dermatomyofibroma (plaque-like dermal fibromatosis). Int J Dermatol 2010; 49: 914–917. - PubMed
-
- Mentzel T, Kutzner H. Dermatomyofibroma: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 56 cases and reappraisal of a rare and distinct cutaneous neoplasm. Am J Dermatopathol 2009; 31: 44–49. - PubMed
-
- Fu S, Zhang J, Zhan Y, Zhang H, Herman EI, Lu Q, et al. . A rare case report for dermatomyofibroma in nasion. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2018; 43: 1037–1040. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T. Dermatofibroma: a possible model of local fibrosis with epithelial/mesenchymal cell interaction. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2009; 23: 371–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

