Burden of overweight and obesity among adolescents in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38850065
- PMCID: PMC11879499
- DOI: 10.1093/inthealth/ihae041
Burden of overweight and obesity among adolescents in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Overweight and obesity continue to escalate, despite the regulations and interventions that have been put in place. To support further policy directions, it is necessary to have pooled data that illustrate the burden of overweight and obesity among adolescents nowadays. Thus, this systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine the burden of overweight and obesity among Ethiopian adolescents.
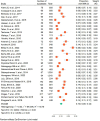
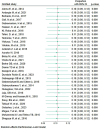
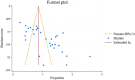
Methods: Embase, Science Direct, Medline, PubMed, Google Scholar and Web of Science were the databases used in the search for publications that ran from inception until 25 October 2023. STATA version 18 was used to analyze data on overweight and obesity in adolescents. Using the random effect model, the pooled estimates with 95% CIs were calculated. Using the Galbraith plot, I2 statistics and Cochrane Q statistics, heterogeneity was investigated.
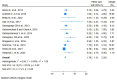
Results: In total, 20145 adolescents aged 10-19 years were included in this meta-analysis study. The pooled prevalence of overweight and obesity among adolescents in Ethiopia was 10% (95% CI 9 to 12%; I2=94.03%). There was a substantial correlation between being female (OR=1.81, 95% CI 1.47 to 2.15), attending private schools (OR=1.78, 95% CI 1.31 to 2.26), having a family size of ≥4 (OR=1.86, 95% CI 1.14 to 2.58) and being of middle economic status (OR=1.62, 95% CI 1.14 to 2.10).
Conclusions: In Ethiopia, one in 10 adolescents is overweight/obese. The study's findings clearly show that a large number of adolescents are dealing with this emerging public health issue. Moreover, characteristics related to physical activity, nutrition and sociodemographics were discovered to be associated with overweight and obesity. To lessen the burden of overweight and obesity, the government and other parties should work together to support gender-specific nutritional interventions, encourage healthy lifestyle choices among teenagers and facilitate these efforts.
Keywords: Ethiopia; adolescents; obesity; overnutrition; overweight.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in regard to this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Magnitude of postpartum hemorrhage and associated factors among women who gave birth in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Reprod Health. 2022 Sep 21;19(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12978-022-01498-4. Reprod Health. 2022. PMID: 36131345 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity, diet and other behavioural interventions for improving cognition and school achievement in children and adolescents with obesity or overweight.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 2;3(3):CD009728. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009728.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29499084 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity, diet and other behavioural interventions for improving cognition and school achievement in children and adolescents with obesity or overweight.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 29;1(1):CD009728. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009728.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 02;3:CD009728. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009728.pub4. PMID: 29376563 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Lifestyle intervention for improving school achievement in overweight or obese children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Mar 14;(3):CD009728. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009728.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 29;1:CD009728. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009728.pub3. PMID: 24627300 Updated.
-
Gender-based violence and associated factors among women in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Womens Health. 2025 Jul 4;25(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s12905-025-03867-0. BMC Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40615840 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of overweight/obesity and its association with fast food consumption among adolescents in Southern Ethiopia, 2022: a community-based cross-sectional study.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 27;11:1475116. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1475116. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39931175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohajan D, Mohajan HK. Obesity and its related diseases: A new escalating alarming in global health. J Innov Medi Res. 2023;2(3):12–23.
-
- Rosales-Ricardo Y, Ortiz-Perez M, Lopez-Merino F et al. Obesity and overweight as an international public health problem. Revis Bionatura. 2023;8(3):15.
-
- WHO . Obesity and Overweight Fact Sheet: Fact Sheet. 2021.
-
- WHO . WHO Obesity and Overweight Fact Sheet 2024. 2024.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

