Daily oral administration of probiotics engineered to constantly secrete short-chain fatty acids effectively prevents myocardial injury from subsequent ischaemic heart disease
- PMID: 38850165
- PMCID: PMC11587561
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvae128
Daily oral administration of probiotics engineered to constantly secrete short-chain fatty acids effectively prevents myocardial injury from subsequent ischaemic heart disease
Abstract
Aims: Given the extremely limited regeneration potential of the heart, one of the most effective strategies to reduce the prevalence and mortality of coronary artery disease is prevention. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are by-products of beneficial probiotics, have been reported to possess cardioprotective effects. Despite their beneficial roles, delivering SCFAs and maintaining their effective concentration in plasma present major challenges. Therefore, in the present study, we aimed to devise a strategy to prevent coronary heart disease effectively by using engineered probiotics to continuously release SCFAs in vivo.
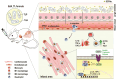
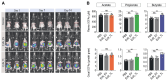
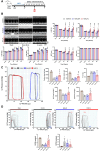
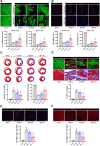
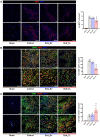
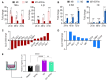
Methods and results: We engineered a novel probiotic cocktail, namely EcN_TL, from the commercially available Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) strain to continuously secrete SCFAs by introducing the propionate and butyrate biosynthetic pathways. Oral administration of EcN_TL enhanced and maintained an effective concentration of SCFAs in the plasma. As a preventative strategy, we observed that daily intake of EcN_TL for 14 days prior to ischaemia-reperfusion injury significantly reduced myocardial injury and improved cardiac performance compared with EcN administration. We uncovered that EcN_TL's protective mechanisms included reducing neutrophil infiltration into the infarct site and promoting the polarization of wound healing macrophages. We further revealed that SCFAs at plasma concentration protected cardiomyocytes from inflammation by suppressing the NF-κB activation pathway.
Conclusion: These data provide strong evidence to support the use of SCFA-secreting probiotics to prevent coronary heart disease. Since SCFAs also play a key role in other metabolic diseases, EcN_TL can potentially be used to treat a variety of other diseases.
Keywords: Coronary heart disease; Myocardial infarction; Prevention; Probiotics; Short-chain fatty acid.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none declared.
Figures


References
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet 2006;367:1747–1757. - PubMed
-
- Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Alonso A, Beaton AZ, Bittencourt MS, Boehme AK, Buxton AE, Carson AP, Commodore-Mensah Y, Elkind MSV, Evenson KR, Eze-Nliam C, Ferguson JF, Generoso G, Ho JE, Kalani R, Khan SS, Kissela BM, Knutson KL, Levine DA, Lewis TT, Liu J, Loop MS, Ma J, Mussolino ME, Navaneethan SD, Perak AM, Poudel R, Rezk-Hanna M, Roth GA, Schroeder EB, Shah SH, Thacker EL, VanWagner LB, Virani SS, Voecks JH, Wang NY, Yaffe K, Martin SS. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2022 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022;145:e153–e639. - PubMed
-
- Gan XT, Ettinger G, Huang CX, Burton JP, Haist JV, Rajapurohitam V, Sidaway JE, Martin G, Gloor GB, Swann JR, Reid G, Karmazyn M. Probiotic administration attenuates myocardial hypertrophy and heart failure after myocardial infarction in the rat. Circ Heart Fail 2014;7:491–499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

